Die Auswahl der richtigen industriellen Batterie ist für die Effizienz von entscheidender Bedeutung, wenn Sie Gabelstapler verwenden, sei es für einen LKW oder eine Flotte. Die entsprechende Elektrogabelbatterie kann langfristig Zeit und Geld sparen.
In diesem Artikel werden wir verschiedene Gabelstaplerbatterien, ihre wichtigsten Unterschiede und Preisbereiche abdecken.
Gabelstaplerbatterie
Während Propan, Diesel und Gas weitere Optionen sind, sind zwei Drittel der Gabelstapler, die jedes Jahr in Betrieb genommen werden, elektrisch.
Elektrische Gabelstapler werden hauptsächlich von zwei Batteriearten angetrieben: Blei- und Lithium-Ionen.
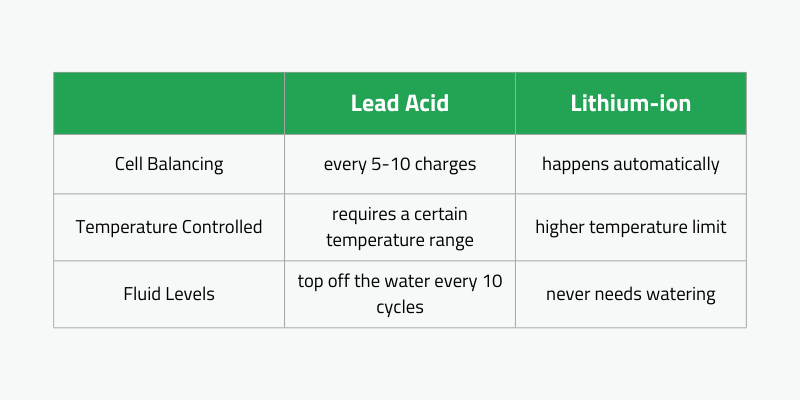
Der Batterietyp beeinflusst die Austauschhäufigkeit: Lithium-Ionen-Batterien können über 3.000 Zyklen aushalten, während Blei-Säure-Batterien etwa 1.500 Zyklen halten. Darüber hinaus müssen Lithium-Ionen-Batterien seltener ausgetauscht werden, weshalb sie für viele Geschäftsinhaber Blei-Säure-Batterien vorzuziehen sind.
Spannungen der Gabelstaplerbatterie
Die Auswahl der Batteriepakete für Gabelstapler richtet sich in der Regel nach der Hubausrüstung und ihrem Verwendungszweck. Es gibt vier gängige Spannungsoptionen:
- 24 V: Geeignet für kleine elektrische Hebegeräte wie End- und Mittelfahrgeräte, Handhubwagen und Handhubwagen.
- 36 V: Konzipiert für mittelgroße Elektrogeräte wie Schmalgangstapler und Stand-Gegengewichtsstapler.
- 48 V: Wird für große elektrische Geräte einschließlich Gegengewichtsstapler verwendet.
- 80 V: Reserviert für schwere Elektrogeräte wie große Gegengewichtsstapler.

Aufladen der Gabelstaplerbatterie
Die Art und Weise, wie die Batterie eines Elektrostaplers aufgeladen wird, wirkt sich auf die Betriebseffizienz und den Bedarf an Ladestationen aus.
Lithium-Ionen-Akkus laden sich schneller auf und können bei Bedarf aufgeladen werden, ohne dass eine vollständige Aufladung erforderlich ist. Im Gegensatz dazu müssen Blei-Säure-Batterien vor dem Abklemmen vollständig geladen werden und können nicht opportunistisch geladen werden.
Beide Typen verschlechtern sich, wenn sie unsachgemäß aufgeladen werden. Für Blei-Säure-Geräte gelten jedoch strengere Richtlinien.
Anforderungen an die Batterieladestation für Gabelstapler
Der Standort Ihres Gabelstapler-Batterieladesystems ist entscheidend.
Blei-Säure-Batterien erfordern spezifische Setups, die Lithium-Ionen-Packungen nicht tun. Lithium-Ionen-Batterien können direkt im Aufzugswagen aufladen, ohne dass zusätzliche Schritte erforderlich sind.
Blei-Säure-Batterien müssen zum Aufladen separater Ladegeräte entfernt werden, die die Ausgleich haben. Unternehmen mit vielen Gabelstapler benötigen mehrere Ladegeräte und Platz für Einheiten, die nach dem Aufladen abkühlen können. Dieser Vorgang ist zeitaufwändig, da Mitarbeiter spezielle Geräte benötigen, um regelmäßig Batterie-Swaps zu verwalten.
Darüber hinaus benötigen Blei-Säure-Ladebereiche aufgrund von Wärme und schädlichen Dämpfen, die während des Lades erzeugt werden. Umgekehrt können Lithium-Ionen-Batterien direkt im Liftwagen aufladen, ohne spezielle Platz oder Kühlperioden zu benötigen. Sie können beim Entladen sofort vor Ort aufladen.

Gabelstapler -Batterie -Wasserversorgungssystem
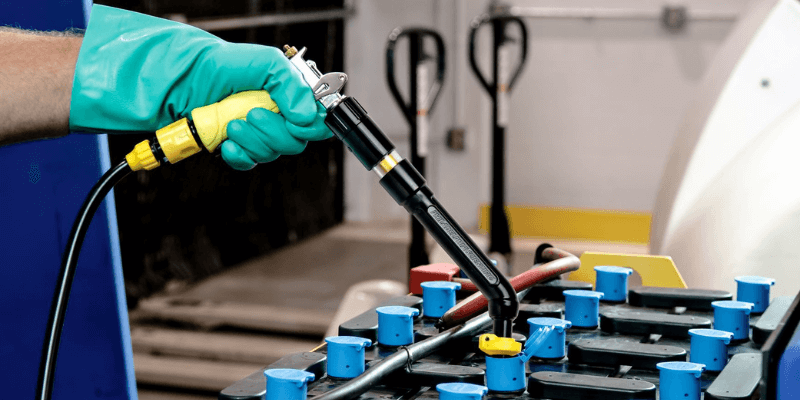
Das Laden ist nicht die einzige Wartung, die für Blei -Säure -Batterien erforderlich ist. Ihre Flüssigkeit braucht regelmäßig Aufmerksamkeit.
Im Gegensatz zu versiegelten Lithium-Ionen-Batterien benötigen Blei-Säure-Batterien ein Bewässerungssystem. Die Mitarbeiter müssen lernen, diese Batterien ordnungsgemäß zu gießen, um eine optimale Leistung und Langlebigkeit zu gewährleisten.
Zu den wichtigsten Praktiken für die Aufrechterhaltung der Blei -Batterie -Batterievergütung gehören:
- Noch nach voll geladenem und abgekühltem Wasser mit Wasser abzahlen.
- Regelmäßig nachfüllen, um die Oberseite der Platten bedeckt zu halten, normalerweise alle 10 Ladungszyklen.
- Vermeiden Sie eine Überfüllung, um während des Gebrauchs eine Flüssigkeitsausdehnung zu ermöglichen.
- Verwenden von Wasser mit einem pH zwischen 5 und 7.
Gabelstaplerbatteriesicherheit
Die Sicherheit ist bei der Behandlung von Gabelstaplerbatterien aufgrund der leistungsstarken Chemikalien von entscheidender Bedeutung. Vergleichen wir Lithium-Ionen- und Blei-Säure-Batterien in Bezug auf die Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz.
Die Sicherheitsrisiken der Blei-Säure-Batterie sind wie folgt:
1. Verschüttungen: Schwefelsäure kann von diesen Batterien verschüttet werden, zumal sie eine wöchentliche Bewässerung erfordern. Unsachgemäßes Handling erhöht das Risiko der Mitarbeiter und erfordert eine chemische Waschstation.
2. Überhitzung: Diese Batterien können beim Laden extrem heiß werden und nach der Spitzenladung explosive Gas auslaufen, was die Temperaturkontrolle für die Sicherheit wesentlich macht.
3. Gefährliche Gase: Überladen kann giftige Gase wie Schwefelwasserstoff, Wasserstoff und Schwefeldioxid in schlecht belüftete Bereiche freisetzen. Ein Geruch nach faulen Eiern weist auf das Vorhandensein von Schwefelwasserstoff hin. Es sollten sofort Vorsichtsmaßnahmen getroffen werden. Installieren Sie standardmäßige katalytische LEL-Gassensoren oder elektrochemische Sensoren in Laderäumen, um den Gasgehalt zu überwachen.
4. Alte oder korrodierte Batterien: Während neue Blei-Säure-Batterien bei korrekter Ladung ein minimales Risiko darstellen, sind alte oder korrodierte Batterien gefährlich und sollten sofort entsorgt werden.
Im Gegenteil, Lithium-Ionen-Gabelstaplerbatterien sind versiegelt, wodurch das Risiko von Säureaustritt oder Korrosion ausgeschlossen ist.

Preise für Gabelstaplerbatterien
Die Gabelstaplerbatteriekosten variieren nach Typ erheblich. Eine Blei-Säure-Batterie liegt zwischen 2.000 und 6.000 US-Dollar, während eine Lithiumbatterie zwischen 17.000 und 20.000 US-Dollar kostet.
Diese Preise spiegeln jedoch nicht die Gesamtbetreuungskosten (TCO) wider. Manager sollten die langfristigen Kosten in Betracht ziehen, die mit jedem Typ verbunden sind, bevor sie eine Entscheidung treffen.
Im Lagerbetrieb sind Arbeitskräfte die größten Kosten, die rechtzeitig gemessen werden. Der Kauf von Bleibbatterien erhöht die Gesamtkosten der Gabelstapler, da für den ordnungsgemäßen Betrieb umfangreiche Mannstunden erforderlich sind. Jede Batterie dauert ungefähr 8 Stunden und benötigt 16 Stunden, um aufzuladen und abzukühlen. Damit müssen mindestens drei Batterien pro Gabelstapler für rund um die Uhr vorhandene Vorgänge erforderlich sind. Für die Wartung werden auch zusätzliche Batterien benötigt, was zu mehr Papierkram und einem engagierten Team für die Verfolgung führt.
Bleibatterien sind groß und erfordern einen ausgewiesenen Stauraum, der das kanadische Zentrum für die Richtlinien für die Gesundheit und Sicherheit des Arbeitsschutzes entspricht und zusätzliche Kosten entspricht. Und spezielle Geräte sind erforderlich, um diese Batterien zu überwachen.
Darüber hinaus besteht ein berufliches Risiko aufgrund ihrer ätzenden Flüssigkeiten. Verschüttungen können den Betrieb einstellen und weitere Zeitkosten entstehen.
Während die anfänglichen Batteriekosten niedrig sind, dauern sie mit ordnungsgemäßer Wartung nur etwa 1.500 Zyklen, was alle 2-3 Jahre sowie die Entsorgungskosten für alte Einheiten ersetzt.
Eine Lithium-Ionen-Gabelstaplerbatterie ist dagegen 55% leichter als Blei-Säure-Batterien und bietet Vorteile wie reduzierter Platzanforderungen, schnelleres Ladevorgang, höhere Energieeffizienz, verbesserte Sicherheit der Arbeit, bessere Kälteleistung und erhöhte Produktivität.
Abschluss
Lithium-Ionen-Batterien bieten zwar ursprünglich teurer, bieten jedoch langfristige Einsparungen durch Effizienz und geringere Wartung. Ihre schnelle Aufladung, Haltbarkeit und Sicherheit machen sie ideal für Gabelstapler.
Berücksichtigen Sie bei der Auswahl zwischen Blei-Säure und Lithium-Ionen Ihre Nutzungsfrequenz- und Sicherheitsbedürfnisse. Eine intelligente Batterieinvestition steigert die Produktivität und reduziert Ausfallzeiten, wodurch Ihr Unternehmen auf dem Markt für Elektroschiffe wettbewerbsfähig bleibt.

