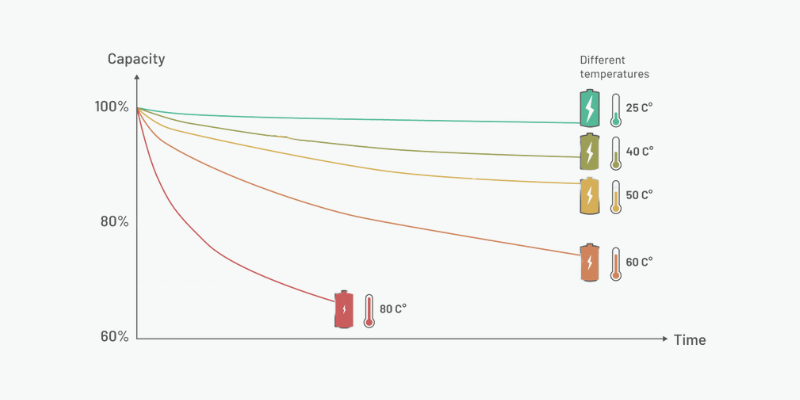
Batterie al litio hanno trasformato l'elettronica portatile e lo stoccaggio di energia rinnovabile con le loro dimensioni compatte ed elevate densità di energiae lunga durata. La temperatura influisce notevolmente sulle loro prestazioni. Questa guida copre gli intervalli operativi ottimali e gli effetti delle temperature estreme.
L'importanza dell'intervallo di temperatura per le batterie al litio
Mantenere l’intervallo di temperatura corretto è fondamentale per ottimizzare l’efficienza e la durata della batteria al litio. Il funzionamento al di fuori di questo intervallo può ridurre la capacità e le prestazioni, accelerare l'invecchiamento e creare rischi per la sicurezza.
Limiti di temperatura della batteria al litio
Le batterie al litio funzionano meglio tra 15°C e 35°C (da 59°F a 95°F), garantendo prestazioni ottimali e una maggiore durata. Al di sotto dei 15°C le reazioni chimiche rallentano, riducendo le prestazioni. Al di sopra dei 35°C, il surriscaldamento può danneggiare la salute della batteria.
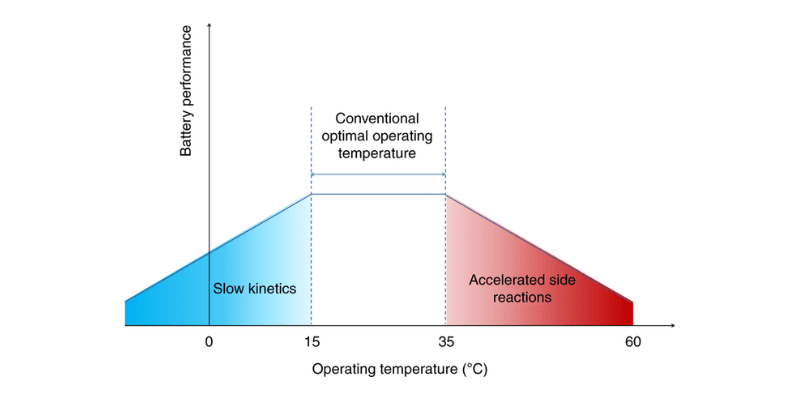
Effetti delle temperature estreme
Le temperature gelide (sotto 0°C o 32°F) danneggiano la batteria elettrolita, mentre le alte temperature (superiori a 60°C o 140°F) accelerano l'invecchiamento e possono causare instabilità termica. Temperature estreme ridurre la durata e l’efficienza della batteria. Gli ambienti controllati e i sistemi di gestione termica mantengono temperature sicure e il monitoraggio regolare previene danni e garantisce la sicurezza.
Temperature di stoccaggio consigliate per le batterie al litio
Intervallo di temperatura di conservazione consigliato
La temperatura di conservazione consigliata per le batterie al litio è generalmente compresa tra -20°C (-4°F) e 25°C (77°F) per mantenere la capacità e ridurre al minimo l'autoscarica. Tuttavia, consulta le linee guida del produttore, poiché le condizioni ottimali possono variare in base al tipo e alla chimica della batteria.
Stoccaggio in climi estremi
La conservazione delle batterie al litio in climi estremi può comprometterne la durata e le prestazioni. Ecco alcuni suggerimenti per una conservazione ottimale:
Climi freddi
- Isolamento: avvolgere la batteria in schiuma o pluriball per evitare cali di temperatura.
- Conservazione riscaldata: conservare la batteria in un'area riscaldata, come un garage o un seminterrato, per mantenerla al di sopra del punto di congelamento.
- Evitare il freddo estremo: limitare l'esposizione a temperature gelide per proteggere i componenti interni.
- Riscaldamento graduale: consentire a una batteria fredda di riscaldarsi gradualmente prima di caricarla o scaricarla.
Climi caldi
- Conservazione in luogo fresco e asciutto: conservare la batteria in un luogo fresco e asciutto, lontano dalla luce solare e dal calore.
- Carica moderata: conservare a una carica pari a circa il 50% per ridurre il degrado.
- Ventilazione: garantire un flusso d'aria adeguato per evitare il surriscaldamento.
- Controlli regolari: monitorare eventuali gonfiori, perdite o odori insoliti.
Carica e scarica della batteria al litio a temperature estreme
Ricarica a temperature estreme
Basse Temperature
- Efficienza di ricarica ridotta: le reazioni chimiche della batteria rallentano, con conseguenti tempi di ricarica più lunghi e capacità ridotta.
- Placcatura al litio: in condizioni di freddo estremo, gli ioni di litio possono formare litio metallico sull'anodo, rischiando cortocircuiti interni e incendi.
- Raccomandazione: evitare di caricare le batterie al litio a una temperatura inferiore a 0°C (32°F). Se necessario, caricarli in un ambiente più caldo.
Temperature elevate
- Invecchiamento accelerato: le alte temperature accelerano l'invecchiamento della batteria, con conseguente esaurimento della capacità e una durata di vita più breve.
- Aumento del rischio di fuga termica: il calore eccessivo può causare fuga termica, con conseguente riscaldamento rapido e potenziale incendio o esplosione.
- Raccomandazione: evitare di caricare batterie al litio a temperature superiori a 45°C (113°F) e utilizzare caricabatterie con sensori di temperatura integrati per regolare la velocità.
Scarica a temperature estreme
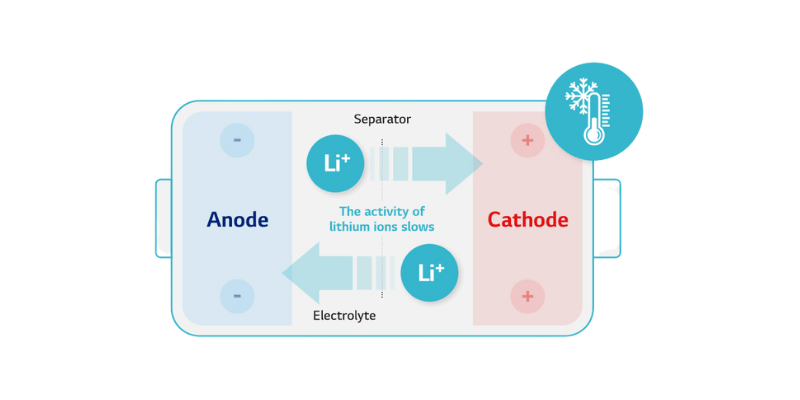
Basse Temperature
- Capacità ridotta: la capacità della batteria diminuisce significativamente alle basse temperature, limitando l'erogazione di potenza.
- Maggiore resistenza interna: le condizioni fredde aumentano la resistenza interna, riducendo le prestazioni.
- Raccomandazione: evitare di scaricare le batterie al litio a una temperatura inferiore a 0°C (32°F). Usateli a brevi intervalli e lasciateli riscaldare prima di un uso prolungato.
Alte temperature:
- Invecchiamento accelerato: le alte temperature accelerano l'invecchiamento della batteria, causando un calo della capacità e una durata di vita più breve.
- Aumento del rischio di fuga termica: il calore eccessivo può anche innescare la fuga termica.
- Raccomandazione: evitare di scaricare le batterie al litio a temperature superiori a 45°C (113°F). Usateli a brevi intervalli e lasciateli raffreddare prima di un uso prolungato.
Strategia per la gestione delle temperature delle batterie al litio
Una gestione efficace della temperatura è fondamentale per ottimizzare le prestazioni e la durata della batteria agli ioni di litio. Ecco alcune strategie:
Tecniche di raffreddamento passivo
- Dissipatori di calore: dissipano il calore attraverso conduzione e radiazione, integrati nel design della batteria per un migliore trasferimento di calore.
- Materiali di interfaccia termica (TIM): migliorano la conduttività termica tra le celle della batteria e i dissipatori di calore utilizzando pasta termica o cuscinetti.
- Ventilazione: facilita il raffreddamento per convezione naturale per dissipare il calore.
Tecniche di raffreddamento attivo
- Raffreddamento a liquido: fa circolare il refrigerante come acqua per rimuovere in modo efficiente il calore dalle celle.
- Raffreddamento ad aria: utilizza le ventole per forzare l'aria sulle celle, accelerando la dissipazione del calore.
- Materiali a cambiamento di fase (PCM): assorbono e rilasciano calore durante le transizioni di fase, tamponando le fluttuazioni di temperatura.
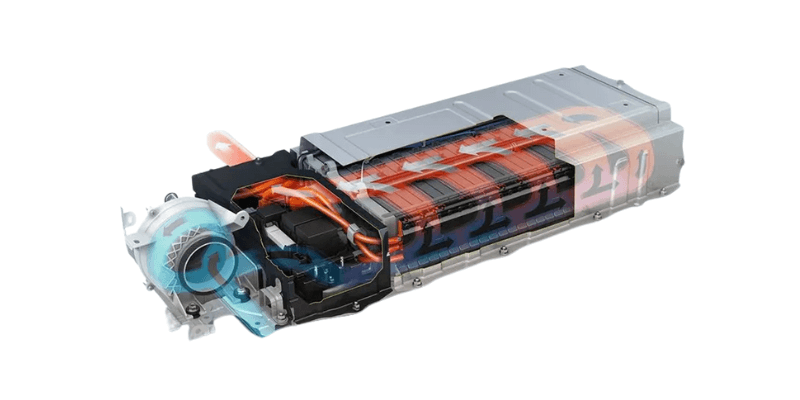
Sistemi di gestione della batteria (BMS)
- Monitoraggio della temperatura: monitora continuamente la temperatura delle singole celle e del pacco.
- Controllo della velocità di ricarica: regola la velocità di ricarica per limitare la generazione di calore, soprattutto durante la ricarica rapida.
- Bilanciamento delle celle: garantisce una distribuzione uniforme della carica tra le celle per evitare temperature irregolari.
- Spegnimento termico: avvia lo spegnimento in casi estremi per proteggere la batteria.
Pratiche degli utenti
- Evitare di esporre le batterie a temperature estreme.
- Velocità di carica e scarica moderate per evitare un'eccessiva generazione di calore.
- Conservare le batterie in un luogo fresco e asciutto con uno stato di carica moderato.
- Seguire regolarmente le raccomandazioni di manutenzione del produttore.
Conclusione
Mantenere la temperatura adeguata per le batterie al litio è vitale per le prestazioni e la longevità. Il funzionamento nell'intervallo consigliato compreso tra 15°C e 25°C (da 59°F a 77°F) garantisce un efficiente accumulo e rilascio di energia. Il rispetto delle linee guida per la conservazione e la gestione efficace della temperatura migliorano l'affidabilità della batteria al litio in varie applicazioni.