Le batterie agli ioni di litio sono essenziali oggi, poiché alimentano dispositivi dagli smartphone ai veicoli elettrici a causa della loro elevata potenza densità di energia e longevità. Tuttavia, le forature possono comportare rischi per la sicurezza. Comprendere questi pericoli, le misure preventive e le risposte alle emergenze è fondamentale per un utilizzo sicuro. Questo articolo esamina le forature della batteria, i relativi rischi e i protocolli di sicurezza.
Quali sono i pericoli derivanti dalla foratura di una batteria agli ioni di litio?
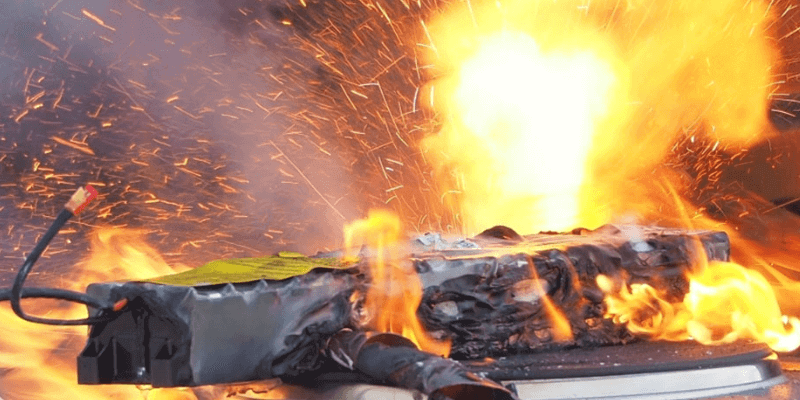
Una batteria agli ioni di litio forata può causare guasti immediati e catastrofici. Il danno fisico crea un cortocircuito interno che innesca una catena di eventi pericolosi.
Fuoco & Combustione
Forare una batteria agli ioni di litio ne danneggia i componenti – anodo, catodoe separatore – causando cortocircuiti e rapida generazione di calore.
Se la temperatura supera i 130°C, fuga termica possono verificarsi, provocando la decomposizione chimica e il rilascio di gas infiammabili. Le temperature possono raggiungere oltre 500°C in pochi minuti, incendiando l'elettrolita e i materiali vicini.
Nelle collisioni di veicoli ad alta velocità, le forze dinamiche aumentano il rischio di esplosione oltre le condizioni di prova standard.
Fumi pericolosi
Le batterie forate rilasciano gas tossici come monossido di carbonio e acido fluoridrico, che sono dannosi se inalati. Questi fumi possono causare problemi respiratori, irritazione della pelle e problemi di salute a lungo termine.
Negli spazi ristretti come le cabine dei veicoli, l’accumulo di gas comporta ulteriori rischi.

I pericoli derivanti dalla foratura delle batterie al piombo
Le forature delle batterie al litio sono spesso considerate pericolose, ma anche le batterie al piombo comportano dei rischi.
Le batterie al piombo sigillate possono perdere acido se forate, causando ustioni e danni alle apparecchiature. Forature gravi possono creare cortocircuiti interni poiché le piastre di piombo entrano in contatto tra loro, generando calore. Ciò potrebbe incendiare la batteria o rilasciare gas di idrogeno solforato infiammabile.
Trattare seriamente tutte le forature della batteria – gli incidenti non sono mai ideali.
Quali tipi di batterie al litio sono resistenti alla perforazione?
Non tutte le batterie agli ioni di litio presentano lo stesso livello di rischio di foratura; dipende dalla loro chimica e costruzione.
Chimica
I principali sono sei tipi di batterie al litio, con il fosfato di litio ferro (LiFePO4) che è tra i più sicuri grazie alla sua bassa resistenza e all'elevata soglia di fuga termica.
Costruzione
Le tre costruzioni primarie sono celle cilindriche, prismatiche e a sacca.
- Le celle cilindriche (ad esempio 18650) sono dotate di involucri metallici per una migliore resistenza alla perforazione.
- Le cellule prismatiche, pur utilizzando gusci duri, hanno ampie aree superficiali soggette a danni.
- Le celle a sacchetto sono più suscettibili alla perforazione poiché i loro componenti si trovano in un sacchetto di alluminio flessibile, che offre poca protezione.
Nessuna batteria è completamente a prova di foratura, ma le scelte progettuali influiscono notevolmente sulla sicurezza.
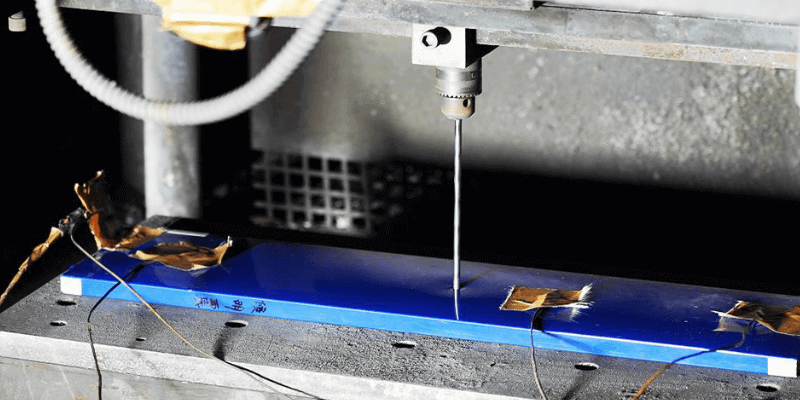
Cosa dovresti fare se la batteria al litio si fora?
Agire rapidamente è importante per ridurre i rischi:
1. Ottenere il flusso d'aria: allontanarsi dalla batteria e garantire una buona ventilazione. Evitare l'inalazione dei fumi.
2. Identificare la batteria: se è sicuro, determinare il tipo di batteria. Quelli cilindrici potrebbero consentire più tempo, ma i tipi a sacca o prismatici richiedono un'azione rapida.
3. Indossare protezioni: se è necessaria la manipolazione, utilizzare guanti e occhiali protettivi. Posizionare la batteria in un contenitore ignifugo lontano da materiali infiammabili.
4. Contattare i professionisti: chiamare i vigili del fuoco o esperti di rifiuti pericolosi per assistenza; non gestire da soli i danni maggiori!
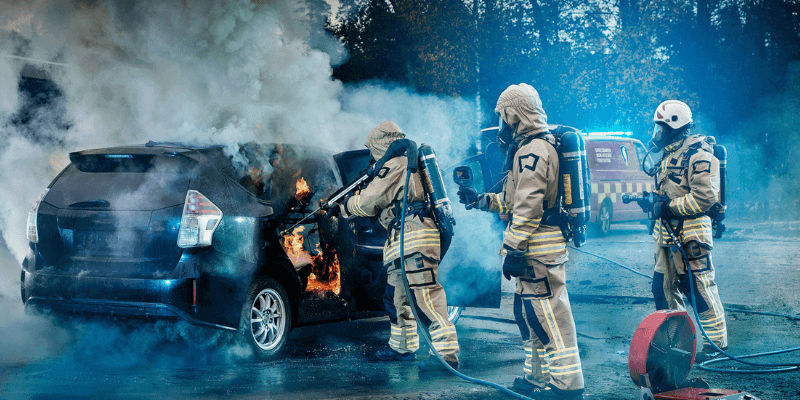
È possibile spegnere l'incendio di una batteria agli ioni di litio?
Evitare l'uso dell'acqua per spegnere l'incendio di una batteria al litio, poiché può generare gas tossici e peggiorare l'incendio.
Innanzitutto, assicurati che tu e i tuoi cari siate al sicuro. Se possibile, utilizzare un estintore ABC standard o un estintore chimico secco – NON è un estintore di Classe D progettato per incendi di metalli combustibili.
Se l'incendio è piccolo e scoppiato precocemente, puoi estinguerlo da solo, ma dai priorità alla tua sicurezza e sappi quando chiamare i professionisti.

Come smaltire in modo sicuro una batteria agli ioni di litio forata?
Uno smaltimento improprio comporta rischi di contaminazione ambientale e incendi durante la lavorazione dei rifiuti:
- Non gettarli nel cestino: le perdite di elettroliti possono avvelenare il suolo e l’acqua.
- Scarica in sicurezza: scarica completamente la batteria per ridurre l'energia immagazzinata.
- Utilizzare strutture designate: consegnarli ai centri di riciclaggio dei rifiuti pericolosi, possibilmente avvolti in sacchetti di plastica trasparente con terminali nastrati.
- Seguire le normative locali: verificare con le agenzie ambientali locali i requisiti specifici.
Le batterie al litio sono sicure e ne valgono la pena?
Sebbene la foratura di una batteria agli ioni di litio comporti qualche rischio, la minaccia per la sicurezza è generalmente bassa rispetto ai suoi benefici. Scegliere le batterie giuste e gestirle correttamente può prevenire incidenti gravi.
Seguendo queste semplici linee guida, puoi affrontare in sicurezza eventuali potenziali incendi e utilizzare le batterie al litio con sicurezza.


