Baterie zasilają urządzenia od smartfonów po samochody, ale mogą tracić pojemność i wydajność z czasem. Testowanie obciążenia baterii rozwiązują te problemy. W tym przewodniku będzie badanie typów, sprzętu i procesu testowania obciążenia baterii.
Co to jest testowanie obciążenia baterii?
Bateria Testowanie obciążenia Mierzy wydajność i zdrowie baterii, stosując kontrolowane obciążenie. Ten test ocenia zdolność baterii do dostarczania energii i utrzymania napięcia w określonych warunkach, co jest niezbędne do oceny niezawodności, identyfikacji problemów i zapobiegania awarii.
Dlaczego testowanie obciążenia baterii jest ważne?
Testowanie obciążenia baterii są ważne z kilku powodów:
- Kontrola jakości: To pomaga producenci Zidentyfikuj i rozwiąż problemy z jakością wcześnie.
- Zaufanie klienta: Testowanie buduje zaufanie konsumentów poprzez udowodnienie, że baterie są bezpieczne i niezawodne.
- Optymalizacja wydajności: Zwiększa wydajność baterii, jednocześnie zmniejszając produkcję koszty.
- Bezpieczeństwo: Testowanie zapobiega awarii, zapewniając bezpieczeństwo w urządzeniach zasilanych baterią.
- Konserwacja: Ocenia, czy bateria działa w granicach i czy jej pojemność maleje.

Zasady testowania obciążenia baterii
Zrozumienie zasad wpływających na test obciążenia baterii ma kluczowe znaczenie dla skutecznych wyników.
Metodologia testowania obciążenia
Testowanie obciążenia udaje baterię do znanego obciążenia przez ustawiony czas trwania podczas monitorowania jego napięcia i wydajności. Kluczowe kroki obejmują:
- Upewnij się, że akumulator jest w pełni naładowany i w zalecanej temperaturze.
- Podłącz akumulator do urządzenia do testowania obciążenia.
- Zastosuj obciążenie na określony czas trwania na podstawie specyfikacji lub standardów branżowych.
- Monitoruj napięcie i wydajność podczas testu.
- Przeanalizuj wyniki, aby ocenić stan akumulatora i określić niezbędne następujące kroki.
Czynniki wpływające na testowanie obciążenia
Kilka czynników może wpływać na dokładność testu obciążenia:
- Temperatura baterii: Zmiany wydajności wraz z temperaturą; test w zalecanych warunkach dla wiarygodnych wyników.
- Załadowany zastosowany: Obciążenie testowe powinno odzwierciedlać oczekiwane wykorzystanie rzeczywistego świata w celu dokładnych ocen.
- Czas trwania: Dopasuj czas testu do specyfikacji; Zbyt krótki może przeoczyć problemy, podczas gdy zbyt długi może uszkodzić baterię.
- Kalibracja sprzętu: Regularna kalibracja sprzętu do testowania zapewnia dokładne pomiary i spójne wyniki.

Typy testowania obciążenia akumulatora
Typowe testy obciążenia obejmują:
1. Test obciążenia prądem stałym: Stosuje stały prąd do pomiaru napięcia w czasie, oceniając pojemność i wydajność.
2. Test obciążenia impulsowego: Poddaje akumulator przerywanym impulsom o wysokim natężeniu, aby ocenić jego reakcję na nagłe obciążenia.
3. Test obciążenia pojemnościowego: Rozładowuje akumulator z określoną szybkością, aż do osiągnięcia wcześniej określonego napięcia, ujawniając użyteczną pojemność i szacunkowy czas pracy.
4. Test obciążenia rozruchowego: Mierzy akumulatory samochodowe’ zdolność do dostarczania wysokiego prądu do rozruchu silnika poprzez ocenę spadku napięcia podczas rozruchu.
Sprzęt do testowania obciążenia akumulatora
Aby wykonać test obciążenia akumulatora, użyj następującego sprzętu:
- Tester obciążenia: Przykłada kontrolowane obciążenie akumulatora, mierząc napięcie, prąd, rezystancję i inne parametry.
- Multimetr: Mierzy napięcie, prąd i rezystancję podczas testu obciążenia w celu zapewnienia dokładności i diagnostyki.
- Rejestrator danych: Rejestruje dane podczas całego testu w celu analizy i porównania w celu określenia trendów wydajności baterii.
- Sprzęt bezpieczeństwa: Aby zminimalizować ryzyko podczas testów, należy nosić rękawice, okulary i odzież ochronną.

Proces testowania obciążenia akumulatora
Aby przeprowadzić test obciążenia akumulatora, wykonaj następujące kroki:
1. Przygotowanie: Naładuj akumulator do pełna, utrzymuj zalecaną temperaturę, zbierz niezbędny sprzęt i zadbaj o bezpieczeństwo.
2. Podłącz sprzęt: Podłącz tester obciążenia i multimetr zgodnie z instrukcjami producenta.
3. Ustaw parametry obciążenia: Skonfiguruj tester obciążenia dla wymaganego obciążenia.
4. Wykonaj test obciążenia: Zastosuj obciążenie przez określony czas trwania podczas monitorowania napięcia i prądu; Zapisz dane, jeśli używasz rejestratora danych.
5. Monitoruj i analizuj: Obserwuj wydajność nieprawidłowości podczas testowania; Następnie przeanalizuj wyniki.
6. Interpretuj wyniki: Porównaj wyniki ze specyfikacjami, aby zidentyfikować problemy i określić niezbędne działania, takie jak wymiana lub konserwacja.
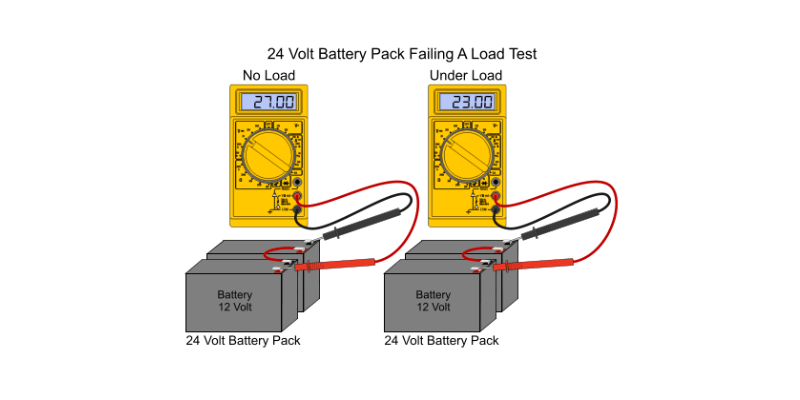
Interpretacja wyników testu obciążenia
Interpretacja wyników testu obciążenia wymaga zrozumienia wydajności baterii.
Kluczowe aspekty obejmują:
- Odpowiedź napięcia: Monitorowanie napięcia podczas testowania; Stabilne napięcie wskazuje na zdrową baterię, podczas gdy znaczne krople mogą sygnalizować pojemność lub problemy z rezystancją.
- Ocena zdolności: Porównaj obserwowaną pojemność z pojemnością znamionową; Znacznie niższa wartość może wskazywać na starzenie lub degradację.
- Analiza wydajności: Oceń wydajność pod obciążeniem dla nadmiernych spadków napięcia i nieregularnych wzorców, które wskazują problemy zdrowotne.
- Trendy i dane historyczne: Porównaj bieżące wyniki z wcześniejszymi danymi, aby zidentyfikować trendy w poprawie wydajności lub spadku.

Wniosek
Testowanie obciążenia baterii są niezbędne do oceny wydajności i zapobiegania awarii. Zrozumienie jego zasad, rodzajów, sprzętu i interpretacji wyników optymalizuje konserwację i zapewnia długoterminową niezawodność.


