Lithium and alkaline batteries are commonly used in household devices and high-performance electronics. This article explores their key differences, such as chemistry, performance, lifespan, and environmental impact. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the best battery type for efficiency and reliability.
Chemistry
There are six types of lithium batteries: LFP, LCO, LMO, NMC, NCA, and LTO.
They are categorized by shape into prismatic and cylindrical cells, and by material into ternary lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate batteries.
The energy stored varies with capacity; for instance, a 4000mAh 32650 LFP cell holds twice the energy of a 2000mAh 18650 NCM cell.
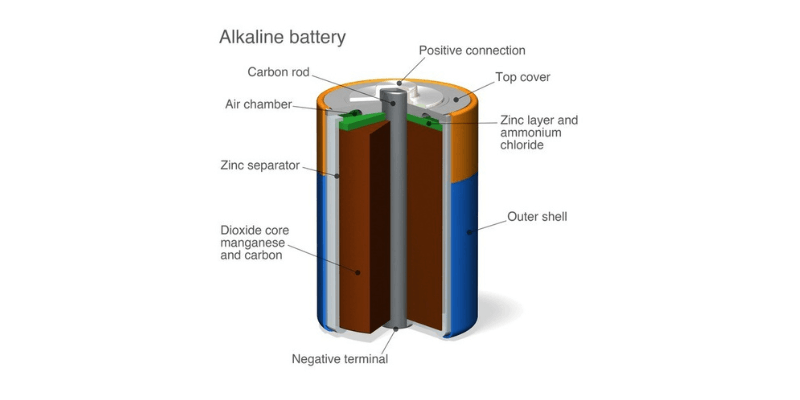
Alkaline batteries rely on zinc and manganese dioxide. When a current is drawn, zinc oxidizes at the anode, and manganese dioxide reduces at the cathode.
Performance
Energy Density
Lithium batteries generally have a higher energy density (over 200 Wh/kg), allowing them to store more energy in less space. This makes them ideal for devices requiring long operating times or compact designs, such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Alkaline batteries, with their lower energy density (80-100 Wh/kg), are better suited for devices with moderate energy demands, such as flashlights, remote controls, and toys.
Self-Discharge Rate
Lithium batteries have a lower self-discharge rate, allowing them to retain their charge longer when not in use. This is especially beneficial for devices stored for extended periods.
In contrast, alkaline batteries have a higher self-discharge rate, causing them to lose charge over time even when unused.
Discharge Rate
Lithium batteries support higher discharge rates, allowing quick power delivery. This is crucial for applications needing sudden energy bursts, such as power tools or cameras.
Alkaline batteries have a lower maximum discharge rate, making them unsuitable for high-current applications.
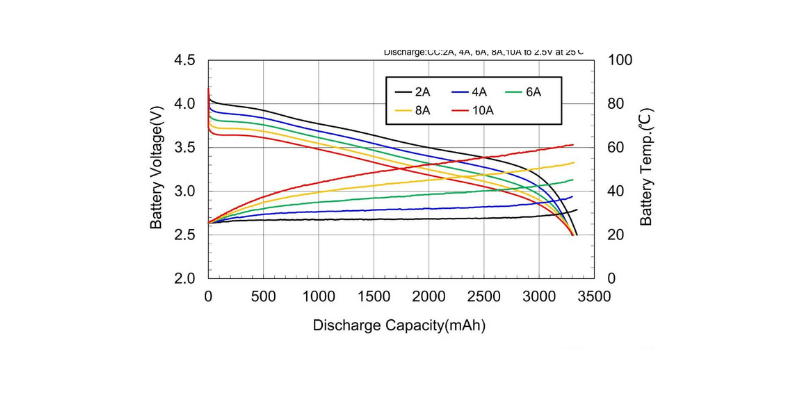
Operating Temperature Range
Lithium batteries operate effectively in a wider temperature range, making them ideal for devices used outdoors or in extreme conditions.
Alkaline batteries have a limited operating temperature range, affecting their performance in extreme conditions.
Voltage
Lithium-ion batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts, though actual voltage may vary slightly by type (e. g., LFP, LCO, NMC).
Alkaline batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, which remains consistent during discharge.
Lifespan
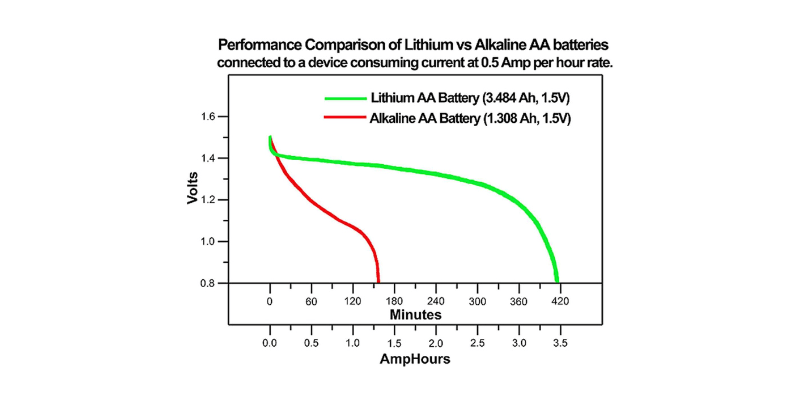
Lithium batteries last eight times longer than alkaline batteries.
Alkaline batteries can last 0.5-1 year, whereas high-quality lithium batteries can last 4-8 years.
Price
Normally, lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront than alkaline batteries.
For instance, a rechargeable lithium-ion AA battery costs $5 to $10 per cell, while alkaline AA batteries are about $0.50 to $1 each.
However, lithium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan.
Environmental Impact
Lithium-ion batteries are more eco-friendly than alkaline batteries because they are rechargeable, reducing waste and resource consumption.
While they require more resources to produce, their durability through hundreds of charging cycles means fewer batteries are needed, lowering environmental impact.
On the contrary, alkaline batteries are single-use and create more hazardous waste.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lithium and alkaline batteries each have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
Lithium batteries offer higher energy density, lower self-discharge rates, and better performance in extreme conditions, making them ideal for high-demand devices like smartphones and electric vehicles. On the other hand, alkaline batteries are better used for moderate energy demands and are commonly used in devices like flashlights and toys.
Understanding the chemistry, performance, lifespan, and environmental impact of these batteries can help you make informed decisions when choosing the best battery type for your needs.