Khi thế giới chuyển sang các nguồn năng lượng mới, sự cạnh tranh giữa pin natri-ion và lithium-ion đang tăng cường. Hiện tại, pin lithium-ion dẫn đầu thị trường, nhưng pin natri-ion đang thu hút sự chú ý do một số lợi thế hấp dẫn. Hãy để khám phá những gì làm cho mỗi người độc đáo, ưu và nhược điểm của họ, và những hướng đi trong tương lai tiềm năng của họ.
Pin natri-ion là gì?
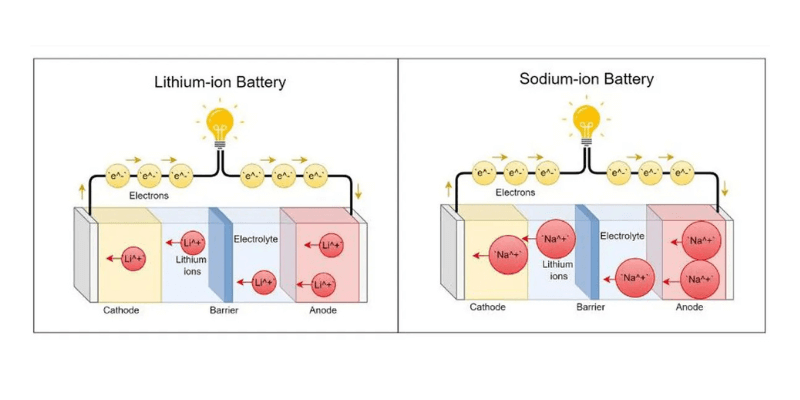
Pin natri-ion (SIB) là pin sạc bằng cách sử dụng các ion natri (NA⁺) làm chất mang điện. Nó bao gồm một catốt có chứa natri, một cực dương và chất điện phân lỏng. Trong quá trình sạc, các ion natri được chiết xuất và chèn vào cực dương, trong khi xả xảy ra đảo ngược.
Có nhiều loại pin natri-ion khác nhau, bao gồm NamNO2, Na3v2 (PO4) 2F3 và Na2Fefe (CN) 6.
Namno₂ (oxit nhiều lớp)
- Điện áp làm việc: 3.2 V; Phạm vi hoạt động: -40 ° C đến 80 ° C.
- Tuổi thọ chu kỳ: Có tới 4.500 chu kỳ trong các nguyên mẫu trong phòng thí nghiệm với tối ưu hóa cấu trúc (ví dụ: doping boron).
- Thách thức: Phân rã công suất nhanh (20 chu kỳ) do chuyển pha Mn³⁺; Biến thể sửa đổi cải thiện sự ổn định.
Na₃v₂ (sau) ₂f₃ (NVPF, loại Nasicon)
- Mật độ năng lượng: 75 WH/kg ở tốc độ 1C; Cao nguyên điện áp cao ở 3,7 V và 4.2 V.
- Tính ổn định của chu kỳ: Hơn 4.000 chu kỳ trong các cấu hình toàn bộ tế bào do lớp phủ carbon và phụ gia điện phân (ví dụ: FEC).
- Ứng dụng: Thích hợp cho lưu trữ lưới và EV do khả năng phục hồi nhiệt và tuổi thọ dài.
Na₂fefe (CN) (Trắng Phổ)
- Hiệu suất: đạt được mật độ năng lượng 160 wh/kg với 3.000 chu kỳ khi kết hợp với cực dương carbon cứng; Lợi ích từ sự khuếch tán nhanh chóng trong một khung khối.
- Ưu điểm: Khả năng tương thích ở nhiệt độ thấp (-20 ° C với khả năng duy trì công suất 80%) và tổng hợp có thể mở rộng, được thương mại hóa bởi CATL.

Pin lithium-ion là gì?
Pin lithium-ion đã phát triển đáng kể trong những năm qua, với lần đầu tiên được phát triển vào những năm 1970. Chúng bao gồm bốn thành phần chính: catốt, cực dương, chất điện phân, và phân tách.
Cathode xác định công suất và điện áp, trong khi cực dương hướng các electron qua một dây. Các chất điện phân Cho phép chuyển động ion lithium giữa cực âm và cực dương cho dòng điện an toàn. Vật liệu dẫn điện ion cao tạo điều kiện cho chuyển động này, thay đổi dựa trên loại chất điện phân.
Có sáu loại pin lithium chính; Thêm thông tin có thể được tìm thấy đây.

Pin natri-ion vs pin lithium-ion
Khi so sánh pin natri-ion và lithium-ion, một bảng so sánh cung cấp một cái nhìn rõ ràng về sự khác biệt của chúng.
| Đặc trưng | Pin natri-ion | Pin lithium-ion |
| Tính khả dụng vật chất | Dồi dào | Giới hạn |
| Tác động môi trường | Thân thiện với môi trường | Ít thân thiện với môi trường hơn |
| Trị giá | Rẻ | Cao |
| Phạm vi nhiệt độ hoạt động | Cao hơn | Cao |
| Vòng đời | Cao | Cao |
| Mật độ năng lượng | Thấp | Cao |
| Thời gian tính phí | Nhanh hơn | Nhanh |
Những thách thức đối với pin natri-ion
Sản xuất pin natri-ion phải đối mặt với một số thách thức trước khi nó có thể thay thế pin lithium-ion.
- Không có chuỗi cung ứng được thiết lập cho vật liệu, và một số công ty có liên quan, dẫn đến chi phí cao hơn.
- Công nghệ này vẫn đang phát triển, hạn chế tính linh hoạt của thiết kế và dẫn đến mật độ và dung lượng lưu trữ thấp hơn so với pin lithium.
- Pin natri-ion có tuổi thọ chu kỳ 5.000 chu kỳ, thấp hơn đáng kể so với 6.000 chu kỳ pin phosphate sắt lithium thương mại.
Pin dựa trên natri có thể thay thế pin lithium-ion không?
Pin natri-ion có thể là một sự thay thế tuyệt vời cho lithium-ion, nhưng chúng phải đối mặt với một số rào cản trước khi chúng thực sự có thể cất cánh.
Để trở thành lựa chọn để lưu trữ năng lượng, họ cần cải thiện hiệu suất kỹ thuật của mình. Các nhà nghiên cứu đang làm việc chăm chỉ để làm cho các pin này ổn định và giá cả phải chăng hơn, trong khi các công ty đang bận rộn thiết lập một chuỗi cung ứng vững chắc cho các vật liệu cần thiết.


