البطاريات تعمل على تشغيل كل شيء من الهواتف إلى السيارات ، مما يجعلها ضرورية في الحياة اليومية. ومع ذلك ، تختلف طاقة البطارية. يعد فهم الجهد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية عند الاختيار بين البطاريات المختلفة. دعونا نستكشف ماهية الجهد ، وكيفية قياسه ، والتفاعلات الكيميائية المعنية.
ما هو جهد البطارية؟
جهد البطارية هو الفرق في الإمكانات الكهربائية بين المحطات الإيجابية والسلبية للبطارية. إنه يمثل الضغط الذي يدفع الإلكترونات من نقطة إلى أخرى.
يمكنك تصور ذلك على شكل زنبرك مضغوط داخل البطارية، حيث يرتبط الضغط الأكبر بزيادة الطاقة الكامنة عند تحريرها. هذه الخاصية ضرورية لتحديد خرج طاقة البطارية، والجهد اللازم للأجهزة، وحالة الشحن.
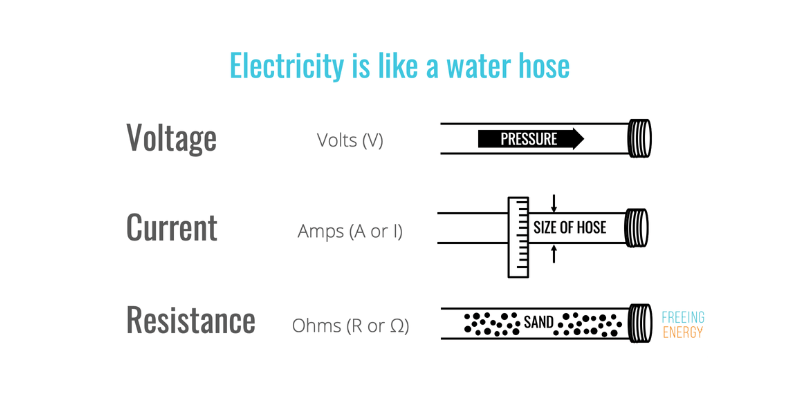
تشبيه آخر هو ضغط الماء في الخرطوم: الجهد الكهربي يدفع الماء عبر الخرطوم (التيار)، ويقاس بالأمبير. تتطلب الأنظمة الكهربائية المختلفة جهدًا كهربائيًا متفاوتًا: 12-48 فولت لأنظمة التيار المستمر المنخفض إلى 110 فولت أو 220 فولت لتطبيقات التيار المتردد السكنية. تعمل الفولتية الأعلى على دفع المزيد من الكهرباء عبر الأسلاك؛ فكر في مدى قوة تيار الماء عالي الضغط.
في حين أن الفولتية المنخفضة (أقل من 50 فولت) آمنة بشكل عام وفقًا لمعايير OSHA ، فإن التيارات الكهربائية في الفولتية الأعلى الموجودة في الشبكات السكنية وخطوط الطاقة يمكن أن تكون خطيرة.

ما الذي يخلق جهد البطارية؟
البطاريات تتكون من الأنود، الكاثود, المنحل بالكهرباءوالفاصل. الأنود هو الجانب السلبي ، عادة ما يكون مصنوعًا من الزنك أو الليثيوم أو الجرافيت أو البلاتين. الكاثود هو النهاية الإيجابية وعادة ما يحتوي على معادن مؤكسدة مثل أكسيد الليثيوم أو أكسيد النحاس.
لا يمكن أن تتدفق الإلكترونات بحرية بين الأنود والكاثود ؛ ومع ذلك ، عند توصيله بواسطة موصل ، تنتقل الإلكترونات من الأنود إلى الكاثود ، مما يولد الجهد.

ما هو الفرق بين الجهد والتيار؟
ترتبط الجهد والتيار ارتباطًا وثيقًا بخصائص مميزة.
- يقيس الجهد الطاقة الكهربائية الكامنة لكل وحدة شحنة، بينما يمثل التيار معدل تدفق الإلكترونات.
- يتم قياس الجهد بالفولت (V) والتيار بالأمبير (A).
- الجهد، الذي يرمز إليه “الخامس،” يدفع التيار داخل الدائرة، بينما التيار، يُشار إليه بـ “أنا،” يدل على تدفق الإلكترونات.
- يعتبر الجهد مستقلا عن الدائرة، في حين يتأثر التيار بمقاومة الدائرة.
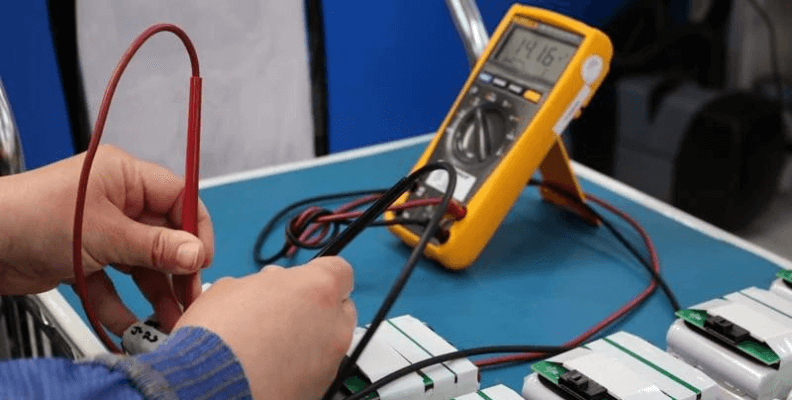
كيف يتم قياس جهد البطارية؟
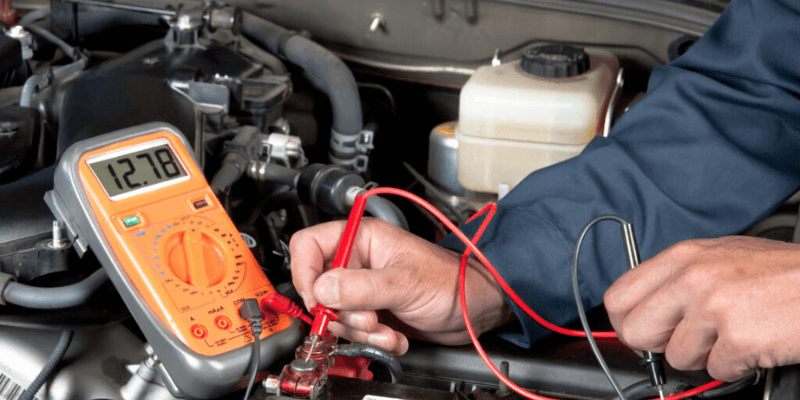
يعد قياس جهد البطارية أمرًا ضروريًا لتحديد حالة الشحن.
أفضل طريقة هي استخدام مقياس متعدد: قم بتوصيل المسبار الأحمر بالطرف الموجب والمسبار الأسود بالطرف السالب، ثم قم بقياس القراءة.

ما هو الجهد الطبيعي؟
يعتمد الجهد الطبيعي للبطارية على نوعها والتفاعل الكيميائي. البطاريات ذات تفاعلات الأكسدة والاختزال الأكثر ملاءمة تنتج فولتات أعلى. على سبيل المثال، يبلغ قياس بطارية السيارة عادةً حوالي 12.6 فولت، بينما يبلغ قياس بطارية AAA حوالي 1.5 فولت.
من الضروري مطابقة الجهد الصحيح لتجنب إتلاف الأجهزة الإلكترونية أو البطارية.
الفولتية الرصاص الحمضية مقابل الفولتية بطارية ليثيوم أيون
يختلف جهد البطارية حسب مستوى الشحن. توفر البطارية المشحونة بالكامل جهدًا أعلى من البطارية المنخفضة أو الفارغة. وتعتمد هذه الظاهرة، المعروفة بفقدان الجهد، على نوع البطارية.
تواجه بطاريات الرصاص الحمضية التقليدية انخفاضًا أكبر في الجهد مقارنة ببطاريات الليثيوم. تعتبر بطاريات الليثيوم، بتقنيتها المتقدمة، أكثر كثافة من حيث الطاقة وأقل تأثراً بها قانون Peukert.
توفر بطارية حمض الرصاص 12 فولت حوالي 12.7 فولت عند شحنها بالكامل و 11.6 فولت بسعة 20 ٪. بالمقارنة ، توفر بطارية الليثيوم 13.6 فولت عند شحنها بالكامل و 12.9 فولت بسعة 20 ٪.
هل جهد البطارية خطير؟
وفق OSHA، لا يعتبر جهد البطارية خطيرًا حتى يتجاوز 50 فولت. يمكن لجسم الإنسان عمومًا أن يتحمل ما يصل إلى 50 فولت من الصدمة دون ضرر ، حيث أن الذراعين والساقين لديهم مقاومة لا تقل عن 500 أوم. تمنع هذه المقاومة التيار المميت من الوصول إلى القلب في معظم الحالات.
ومع ذلك ، فإن الفولتية التي تتجاوز 50 فولتًا يمكن أن تجعل الجسم موصلًا ، مما يشكل مخاطر خطيرة بما في ذلك الحروق ، والعظام المكسورة ، وفقدان السمع ، وإصابات العين ، والسكتة القلبية ، والموت. حتى 10 مللي أمهات من خلال القلب يمكن أن يعطل الموصلية الكهربائية ويسبب عدم انتظام ضربات القلب المميت ؛ وبالتالي فإن جميع الفولتية التي تزيد عن 50 فولت تعتبر خطرة.
لماذا يهم جهد البطارية؟
يعد جهد البطارية أمرًا مهمًا لأنه يشير إلى مقدار الطاقة التي يمكن أن توفرها البطارية ، مما يساعد على تحديد الجهد المطلوب للإلكترونيات وحالة الشحن الخاصة بهم. دون قياس جهد البطارية ، سيكون استخدام البطاريات بأمان مستحيلًا.