Lithium-based battery packs require a Battery Management System (BMS) to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, voltage, current, charge/discharge rates, capacity, and overall health. If issues like overheating or overcharging are detected, the BMS alerts the main control system to initiate cooling or halt charging. Therefore, reliable communication protocols between the BMS, the device, and the control system are fundamental to operational safety and efficiency.
Types of Battery Communication Protocols
Several communication protocols are commonly used today, each with specific strengths:
- RS232 is for short-distance, point-to-point connections like diagnostics or firmware updates. It’s simple but supports only one device and works best up to 15-20 meters.
- RS485 handles longer distances (up to 1, 200 meters), connects multiple devices on one network. It is reliable in noisy environments – ideal for home energy systems with several batteries.
- CAN (Controller Area Network), originally developed for cars and now used in advanced energy systems, supports high-speed multi-device communication with error detection. It’s robust but more complex to set up, suitable for large-scale or commercial applications requiring real-time data exchange.
- Other protocols like I2C, SMBus, and UART serve smaller devices (e. g., consumer drones) with simpler needs. Wireless protocols such as BLE are used for short-range monitoring.
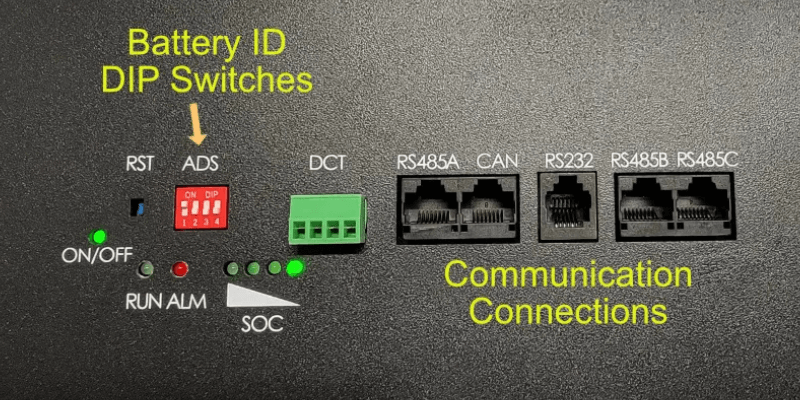
Choosing the Right Communication Protocol
Choosing the right protocol depends on your specific needs. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Your choice should be based on the scale of your system and what you need it to do.
Here is a quick comparison of three common protocols to help you decide:
Protocol Max Distance Speed Best For
| Protocol | Max Distance | Speed | Best For |
| RS232 | 15-20m | Up to 115 kbps | Diagnostics, simple setups |
| RS485 | 1,200m | Up to 10 Mbps | Home systems with multiple batteries |
| CAN | 40m (at 1Mbps) | Up to 1 Mbps | Large-scale, real-time applications |
For most multi-battery home systems, RS485 is a good choice. For larger, high-performance setups, CAN is often better despite its complexity. Ensure your battery’s BMS and inverter use the same protocol to avoid communication failures and system issues.
Purpose of a Battery Communication Protocol
The main job of a communication protocol is to enable data exchange. It allows the Battery Management System (BMS) to share important information with other devices, such as inverters or monitoring systems. Typically, this data includes:
- Voltage and current
- Temperature
- State of Charge (SoC) – how much energy is left
- State of Health (SoH) – the overall condition of the battery
- Alarm or fault messages
This ongoing data serves three key purposes:
- Enhances Safety: The BMS can signal the inverter to stop charging if the battery is full, preventing dangers like overcharging or overheating.
- Improves Efficiency: Accurate data helps optimize charge and discharge cycles for better battery use.
- Prolongs Battery Life: Balanced operation and precise monitoring reduce wear and tear, extending battery life.
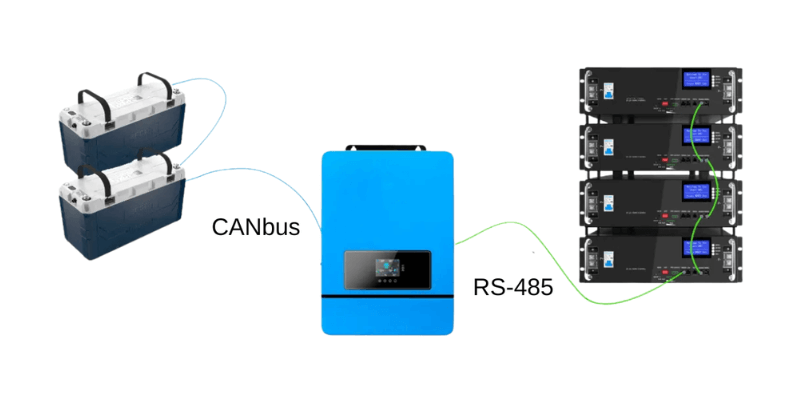
Communication Format Guidelines
For smooth communication, everyone in the system must follow the same communication format.
Flow and Sequential Guidelines
Data is sent in organized packets with an address, message, and error-checking method. Protocols define the structure of these data frames.
For example, the CAN protocol uses a frame format with an identifier (priority code), data, and checksum for errors. Communication often follows a sequence; a master device like a computer may request information from slave devices such as batteries in a specific order.
Transmission Fault Detection Guidelines
Data transmission can fail. Protocols have built-in methods to detect these faults. A common method is a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). This is a mathematical calculation added to the end of the data packet.
The receiving device performs the same calculation. If the results differ, it knows the data was corrupted during transmission. The protocol then dictates what to do next, like asking for the data to be sent again. This ensures the information is reliable.
Addressing and Acknowledgment Guidelines
In a network with multiple devices, each one needs a unique “address.” This ensures that messages get to the right place. For instance, in a Modbus network, each battery might have a unique address from 0x01 to 0x0A.
Acknowledgment is a way to confirm a message was received. Some protocols use a system where the receiving device sends back an “acknowledgment” message. If the sender doesn’t receive an acknowledgment, it resends the message for more reliable communication.
Conclusion
Battery communication protocols are essential for safe and efficient energy systems. They act as the vital link between the battery, its management system, and other components.
Choosing the right protocol depends on your system’s size and needs. RS485 is often a good fit for homes, while CAN is better for large-scale applications. The key is to ensure compatibility between all parts of your system and to follow established guidelines for data flow, error checking, and addressing.
By enabling critical data exchange, these protocols help prevent accidents, maximize performance, and extend the life of your battery investment.


