Den voksende efterspørgsel efter mindre, lettere og mere kraftfulde bærbare elektronik afhænger af fremskridt i Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteri teknologi. At designe batteripakker til moderne enheder kræver afbalancering af energitæthed, sikkerhed, størrelse, vægt, omkostninger og lovgivningsmæssig overholdelse.
Batteripakke -dimension og vægtbegrænsninger
Større batteripakker leverer normalt højere strøm i længere varighed.
Imidlertid står bærbare enheder over for vægt og pladsbegrænsninger, hvilket kræver, at producenterne designer lette pakker, der stadig giver betydelig strøm.
Lithium-ion-batterier fås i forskellige formater til disse enheder, herunder Cylindrisk, prismatiskog posepolymerceller.
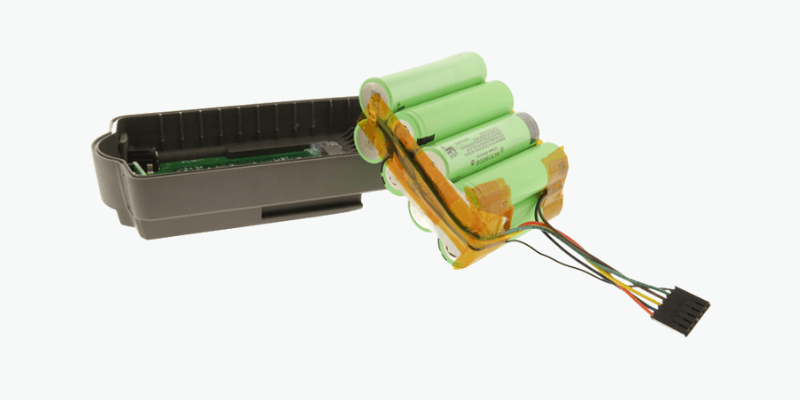
Cylindriske celler (f.eks. 18650, 26650, 21700)
Cylindriske celler er med moden fremstilling, høj specifik energi (200-260 WH/kg), fremragende termisk styring og omkostningseffektivitet. Men deres stive form begrænser volumetrisk energitæthed (500-600 WH/L) og designfleksibilitet.
Integrering af flere celler tilføjer kompleksitet og ineffektiv plads. De bruges ofte i bærbart medicinsk udstyr, håndholdte kommercielle og militære værktøjer og elværktøj.
Prismatiske celler
Prismatiske celler har et rektangulært hus og tilbyder typisk højere volumetrisk energitæthed (600-700 WH/L) end cylindriske celler på grund af bedre pladsudnyttelse.
De har mellemliggende designfleksibilitet, men kan have lidt lavere specifik energi (160-220 WH/kg) og højere omkostninger pr. KWh. Termisk styring kan også være mere udfordrende.
Polymerceller (poseceller)
Polymerceller har fleksible aluminiumlaminatbeklædninger og høj volumetrisk energitæthed (600-800 Wh/L), hvilket gør dem velegnede til tynde eller uregelmæssige former.
De tilbyder et godt vægt-til-kapacitet-forhold (250-300 Wh/kg), men mangler mekanisk stivhed og har brug for stærk strukturel støtte.
Udfordringerne omfatter termisk styring og produktionsomkostninger. Disse celler bruges ofte i bærbare enheder som wearables, medicinsk udstyr, droner, bærbare computere og tablets.
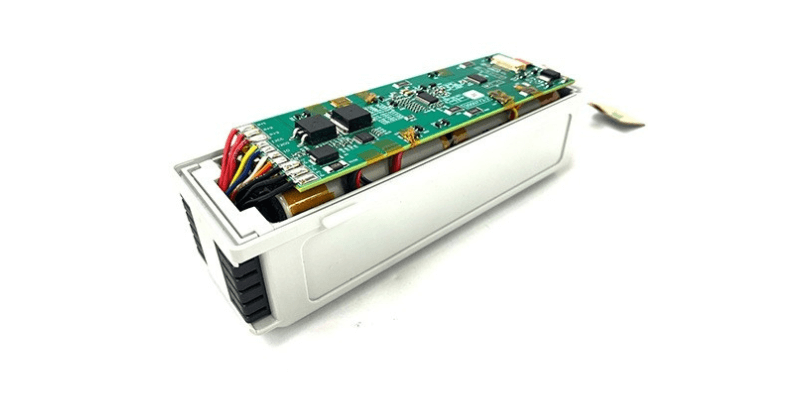
Watt-timers begrænsninger
En vigtig designparameter er den samlede energikapacitet, målt i watt-timer (Wh = spænding * ampere-timer). Forøgelse af Wh forlænger driftstiden, men øger også størrelse, vægt og omkostninger.
Sikkerhedsregler sætter strenge grænser for Wh for flyrejser: Celler under 20 Wh og Batteripakker under 100 Wh er tilladt uden begrænsninger.
Pakker mellem 100-160 Wh kræver flyselskabsgodkendelse, med maksimalt to per passager eller reservedele. Pakninger over 160 Wh er typisk forbudt som håndbagage. Disse regler påvirker markant den maksimale energi, der er tilgængelig for højtydende ultraportables som premium bærbare computere.
Opladningsdesignmuligheder
Opladning af lithium-ion-batterier kræver specifikke parametre.
I modsætning til andre batterier har de brug for dedikerede opladere på grund af producentens designvariationer, der påvirker strøm- og spændingsindstillinger.
Med lavere modstand muliggør lithium-ion-celler hurtigere opladning, så opladere skal levere den korrekte strøm uden over- eller underopladning. Brugerdefinerede opladere til specifikke batteripakker foretrækkes frem for hyldemodeller.

BMS designs
Batteristyringssystemer (BMS) beskytter lithium-ion-batterier mod problemer som høje temperaturer, overopladning, underopladning og termisk flugt. Forskrifter påbyder BMS-installation for alle Lithiumbaserede batterier, herunder bærbare enheder.
For bærbare computere omfatter BMS-funktioner temperaturovervågning, overop- og afladningsstyring og fejldiagnose.
Interoperabilitet er også afgørende for at kommunikere batteritilstand på tværs af netværk og controllersystemer.
Kabinettes særlige funktioner
Sikkerhed er afgørende for bærbare enheder, der bruger lithium-ion-batterier. Disse batterier skal beskyttes mod punkteringer og beskadigelse, hvis enheden tabes eller håndteres forkert.
Kredsløbsbeskyttelse, ligesom polymere positive temperaturkoefficienter (PPTC) enheder, kan beskytte kredsløb under forsendelse og transport.
Indkapslinger beskytter også lithium-ion-batterier mod stød og vibrationer, mens de tillader gasudluftning og varmeafledning.
Producenter tilbyder forskellige indkapslingsmuligheder, herunder krympefolie, vakuumformet plastik og sprøjtestøbt plast, som gennemgår sikkerhedsfaldstest for at sikre holdbarhed og pålidelighed.
Transportabilitetsbestemmelser
Transportregler for lithium-ion-batterier gælder for både bærbare og ikke-bærbare enheder.
Alle lithium-batterier skal medfølge BMS komponenter, uanset om de sendes separat eller installeret. De er begrænset til maksimalt 100 watt-timer, medmindre de er godkendt af operatøren. Bærbare enheder kræver sikkerhedstest og certificering.
Fra januar 2026 skal lithium-ion-batterier, der sendes alene, have en ladetilstand (SoC) på 30 % eller mindre. Derudover skal emballage til ikke-specifik forsendelse opfylde 3,0 meter stak-testen, hvis den indeholder batterier i eller pakket med enheder.
Konklusion
Design af lithium-ion batteripakker til bærbare enheder afhænger af enhedens behov, industristandarder (såsom dem til medicinsk eller militær brug) og nødvendige regler. EN Brugerdefineret batteripakkeproducent som Holo Battery kan hjælpe med at bestemme den rigtige teknologi og funktioner for at sikre, at din batteripakke fungerer effektivt, forbliver pålidelig og sikker.