Las baterías alimentan los dispositivos de teléfonos inteligentes hasta automóviles, pero pueden perder capacidad y rendimiento con el tiempo. La prueba de carga de la batería aborda estos problemas. Esta guía explorará los tipos, el equipo y el proceso de las pruebas de carga de la batería.
¿Qué es una prueba de carga de batería?
Batería prueba de carga Mide el rendimiento y la salud de una batería aplicando una carga controlada. Esta prueba evalúa la capacidad de la batería para ofrecer energía y mantener voltaje en condiciones específicas, lo cual es esencial para evaluar la confiabilidad, identificar problemas y prevenir fallas.
¿Por qué las pruebas de carga de batería son importantes?
La prueba de carga de la batería es importante por varias razones:
- Control de calidad: Ayuda fabricantes Identificar y abordar los problemas de calidad temprano.
- Confianza del cliente: Las pruebas generan confianza en los consumidores al demostrar que las baterías son seguras y confiables.
- Optimización del rendimiento: Mejora el rendimiento de la batería al tiempo que reduce la producción. costos.
- Seguridad: Las pruebas previenen fallas, garantizando la seguridad en los dispositivos que funcionan con baterías.
- Mantenimiento: Evalúa si una batería funciona dentro de los límites y si su capacidad está disminuyendo.

Principios de prueba de carga de batería
Comprender los principios que influyen en las pruebas de carga de la batería es crucial para obtener resultados efectivos.
Metodología de prueba de carga
Las pruebas de carga someten una batería a una carga conocida durante un período determinado mientras monitorean su voltaje y rendimiento. Los pasos clave incluyen:
- Asegúrese de que la batería esté completamente cargada y a la temperatura recomendada.
- Conecte la batería para cargar el equipo de prueba.
- Aplique la carga durante un tiempo predeterminado según las especificaciones o los estándares de la industria.
- Monitoree el voltaje y el rendimiento durante la prueba.
- Analice los resultados para evaluar el estado de la batería y determinar los siguientes pasos necesarios.
Factores que afectan las pruebas de carga
Varios factores pueden afectar la precisión de la prueba de carga:
- Temperatura de la batería: El rendimiento cambia con la temperatura; Pruebe bajo las condiciones recomendadas para obtener resultados confiables.
- Carga aplicada: La carga de pruebas debe reflejar el uso esperado en el mundo real para realizar evaluaciones precisas.
- Duración de la prueba: Hacer coincidir la duración de la prueba con las especificaciones; demasiado corto puede pasar por alto problemas, mientras que demasiado largo puede dañar la batería.
- Calibración del equipo: La calibración regular de los equipos de prueba garantiza mediciones precisas y resultados consistentes.

Tipos de pruebas de carga de batería
Las pruebas de carga comunes incluyen:
1. Prueba de carga de corriente constante: Aplica una corriente estable para medir el voltaje con el tiempo, evaluando la capacidad y el rendimiento.
2. Prueba de carga de pulso: Sujetos la batería a pulsos intermitentes de alta corriente para evaluar su respuesta a cargas repentinas.
3. Prueba de carga de capacidad: Descarga la batería a una velocidad específica hasta alcanzar un voltaje predefinido, revelando la capacidad utilizable y las estimaciones de tiempo de ejecución.
4. Prueba de carga de arranque: Mide las baterías automotrices’ Capacidad para entregar una corriente alta para el motor que comienza mediante la evaluación de la caída de voltaje durante el arranque.
Equipo de prueba de carga de batería
Para realizar una prueba de carga de batería, use el siguiente equipo:
- Tester de carga: Aplica una carga controlada a la batería, midiendo el voltaje, la corriente, la resistencia y otros parámetros.
- Multímetro: Mide el voltaje, la corriente y la resistencia durante la prueba de carga de precisión y diagnóstico.
- Registrador de datos: Registra datos a lo largo de la prueba para el análisis y la comparación para identificar las tendencias de rendimiento de la batería.
- Equipo de seguridad: Use guantes, gafas y ropa protectora para minimizar los riesgos durante las pruebas.

Proceso de prueba de carga de batería
Para realizar una prueba de carga de batería, siga estos pasos:
1. Preparación: Cargue completamente la batería, mantenga la temperatura recomendada, recopile el equipo necesario y garantice la seguridad.
2. Conecte el equipo: Adjunte el probador de carga y el multímetro de acuerdo con las instrucciones del fabricante.
3. Establecer parámetros de carga: Configure el probador de carga para la carga requerida.
4. Realizar prueba de carga: Aplique la carga para una duración especificada mientras monitorea el voltaje y la corriente; Registre datos si usa un registrador de datos.
5. Monitorear y analizar: Observe el rendimiento de las anormalidades durante las pruebas; Analice los resultados después.
6. Interpretar los resultados: Compare los resultados con especificaciones para identificar los problemas y determinar las acciones necesarias como el reemplazo o el mantenimiento.
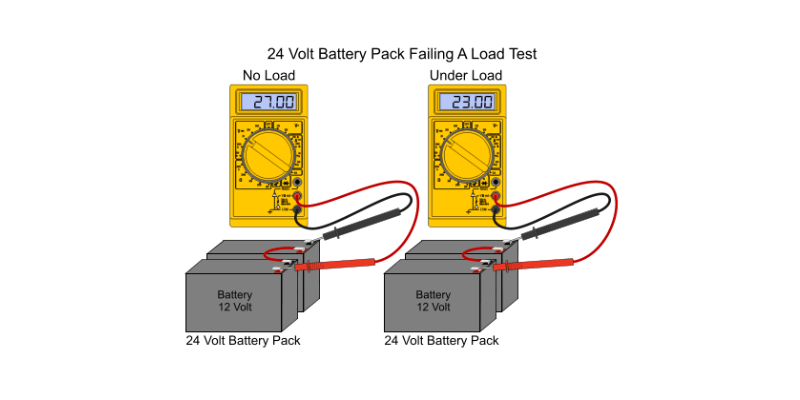
Interpretando los resultados de las pruebas de carga
La interpretación de los resultados de las pruebas de carga requiere comprender el rendimiento de la batería.
Los aspectos clave incluyen:
- Respuesta de voltaje: Monitorear el voltaje durante la prueba; El voltaje estable indica una batería sana, mientras que las caídas significativas pueden indicar problemas de capacidad o resistencia.
- Evaluación de la capacidad: Compare la capacidad observada con la capacidad nominal; Un valor significativamente más bajo puede indicar envejecimiento o degradación.
- Análisis de rendimiento: Evalúe el rendimiento bajo carga para gotas de voltaje excesivas y patrones irregulares, que indican problemas de salud.
- Tendencias y datos históricos: Compare los resultados actuales con datos pasados para identificar las tendencias en la mejora del rendimiento o la disminución.

Conclusión
La prueba de carga de la batería es esencial para evaluar el rendimiento y prevenir fallas. Comprender sus principios, tipos, equipos e interpretación de resultados optimiza el mantenimiento y garantiza la confiabilidad a largo plazo.

