Elegir la batería industrial adecuada es vital para la eficiencia al usar carretillas elevadoras, ya sea para un camión o una flota. La batería de carretillas elevadoras eléctricas apropiadas puede ahorrar tiempo y dinero a largo plazo.
En este artículo, cubriremos varias baterías de montacargas, sus diferencias clave y los rangos de precios.
Tipos de batería de montacargas
Mientras que el propano, el diesel y el gas son otras opciones, dos tercios de las carretillas elevadoras colocadas en servicio cada año son eléctricas.
Las carretillas elevadoras eléctricas están alimentadas principalmente por dos tipos de baterías: iones de plomo y litio.
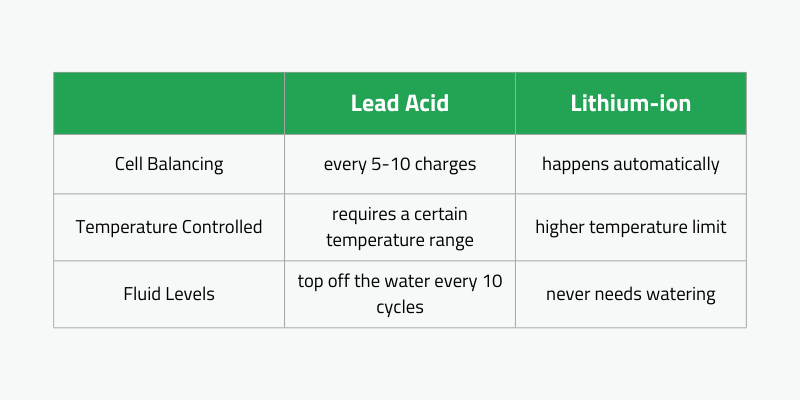
El tipo de batería afecta la frecuencia de reemplazo: las baterías de iones de litio pueden soportar más de 3.000 ciclos, mientras que las baterías ácidas de plomo duran alrededor de 1,500 ciclos. Además, las baterías de iones de litio requieren un reemplazo menos frecuente, lo que las hace preferibles para liderar las baterías ácidas para muchos dueños de negocios.
Voltajes de la batería de la carretilla elevadora
Los paquetes de baterías de la carretilla elevadora se eligen generalmente en función del equipo de elevación y su uso previsto. Hay cuatro opciones de voltaje comunes:
- 24V: Adecuado para pequeños equipos de elevación eléctrica como jinetes finales, jinetes centrales, apiladores de walkie y gatos de paletas de walkie.
- 36V: diseñado para equipos eléctricos de tamaño medio, como carretillas elevadoras de pasillo estrecho y carretillas elevadoras de pie de pie.
- 48V: Se utiliza para equipos eléctricos grandes, incluidos elevadores contrarrestados.
- 80V: Reservado para equipos eléctricos de servicio pesado como grandes carretillas elevadoras contradalancadas.

Carga de la batería de la carretilla elevadora
La forma en que se recarga la batería de un camión de elevación eléctrica afecta la eficiencia operativa y las necesidades de la estación de carga.
Las baterías de iones de litio se cargan más rápido y se pueden cargar de manera oportunista sin necesidad de una recarga completa. Por el contrario, las baterías de plomo-ácido deben cargarse por completo antes de desconectarse y no se pueden cargar de manera oportunista.
Ambos tipos se deterioran si se cargan incorrectamente, pero las unidades de plomo-ácidos tienen pautas más estrictas.
Requisitos de la estación de carga de la batería de la carretilla elevadora
La ubicación del sistema de carga de batería de la carretilla elevadora es crucial.
Las baterías de plomo-ácido requieren configuraciones específicas que los paquetes de iones de litio no. Las baterías de iones de litio pueden cargarse directamente mientras aún están en el camión de elevación, sin necesidad de pasos adicionales.
Las baterías de plomo-ácido deben eliminarse para cargar en cargadores separados capaces de igualar. Las empresas con muchas carretillas elevadoras necesitan múltiples cargadores y espacio para que las unidades se enfríen después de la recarga. Este proceso lleva mucho tiempo, ya que los empleados necesitan equipos especiales para administrar los intercambios de baterías regularmente.
Además, las áreas de carga de plomo-ácido necesitan una ventilación adecuada debido al calor y los vapores nocivos producidos durante la carga. Por el contrario, las baterías de iones de litio pueden cargarse directamente en el camión de elevación sin necesidad de espacio dedicado o períodos de enfriamiento. Pueden recargarse inmediatamente en el sitio cuando se descargan.

Sistema de riego de batería de montacargas
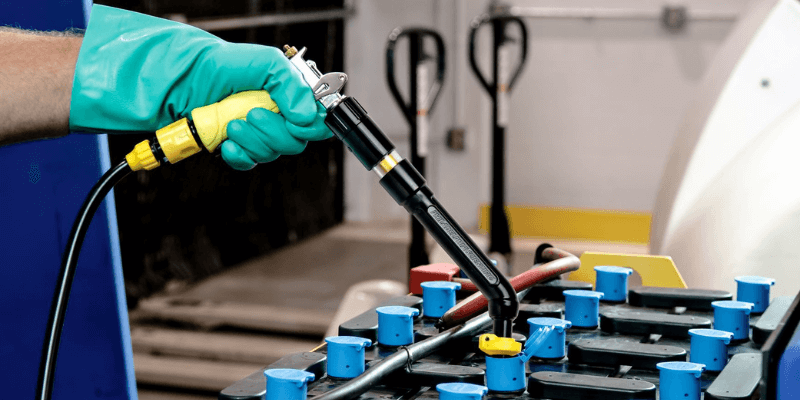
La carga no es el único mantenimiento requerido para las baterías ácidas de plomo; Su fluido necesita atención regular.
A diferencia de las baterías selladas de iones de litio, las baterías ácidas de plomo requieren un sistema de riego. Los empleados deben aprender a regar adecuadamente estas baterías para garantizar un rendimiento y longevidad óptimos.
Las prácticas clave para mantener el riego de la batería de la carretilla elevadora de ácido de plomo incluyen:
- Cubra con agua solo después de cargar y enfriar completamente.
- Rellenarse regularmente para mantener la parte superior de las placas cubiertas, generalmente cada 10 ciclos de carga.
- Evitar el sobrecargador para permitir la expansión de líquido durante el uso.
- Usar agua con un pH entre 5 y 7.
Seguridad de la batería de la carretilla elevadora
La seguridad es crucial al manejar las baterías de la carretilla elevadora debido a los potentes productos químicos involucrados. Comparemos las baterías de iones de litio y de plomo en términos de seguridad en el lugar de trabajo.
Los riesgos de seguridad de la batería de plomo-ácido son los siguientes:
1. Derrames: el ácido sulfúrico puede derramarse de estas baterías, especialmente porque requieren riego semanal. El manejo inadecuado aumenta el riesgo de los empleados, lo que requiere una estación de lavado químico.
2. Sobrecalentamiento: estas baterías pueden calentarse mucho mientras se cargan y pueden filtrar gas explosivo después de la carga máxima, lo que hace que el control de temperatura sea esencial para la seguridad.
3. Gases peligrosos: la sobrecarga puede liberar gases tóxicos como sulfuro de hidrógeno, hidrógeno y dióxido de azufre en áreas mal ventiladas. Un olor a huevo podrido indica la presencia de sulfuro de hidrógeno; Se deben tomar precauciones inmediatas. Instale sensores de gas LEL catalíticos estándar o sensores electroquímicos en salas de carga para monitorear los niveles de gas.
4. Batinas antiguas o corroídas: mientras que las nuevas baterías de plomo-ácido representan un riesgo mínimo si se cargan correctamente, las viejas o corroídas son peligrosas y deben eliminarse de inmediato.
Por el contrario, las baterías de la carretilla elevadora de iones de litio están selladas, eliminando los riesgos de derrames ácidos o corrosión.

Precio de la batería de la carretilla elevadora
Los costos de la batería de la carretilla elevadora varían significativamente por tipo. Una batería de plomo-ácido varía de $ 2,000 a $ 6,000, mientras que una batería de litio cuesta entre $ 17,000 y $ 20,000.
Sin embargo, estos precios no reflejan el costo total de propiedad (TCO). Los gerentes deben considerar los gastos a largo plazo asociados con cada tipo antes de tomar una decisión.
En las operaciones de almacén, la mano de obra es el costo más grande, medido en el tiempo. La compra de las baterías de plomo-ácido aumentará los costos generales de la carretera elevadora, ya que requieren horas de hombre extensas para un funcionamiento adecuado. Cada batería dura aproximadamente 8 horas y necesita 16 horas para cargar y enfriar, lo que requiere al menos tres baterías por carretilla elevadora para operaciones las 24 horas, los 7 días de la semana. También se necesitan baterías adicionales para el mantenimiento, lo que lleva a más papeleo y un equipo dedicado para el seguimiento.
Las baterías de plomo-ácido son grandes y requieren espacio de almacenamiento designado que cumpla con el Centro Canadiense para las Directrices de Seguridad y Salud Ocupacional, incurriendo en costos adicionales. Y es necesario equipos especializados para monitorear estas baterías.
Además, existe un riesgo ocupacional debido a sus líquidos corrosivos; Los derrames pueden detener las operaciones e incurrir en costos de tiempo.
Si bien los costos iniciales de la batería son bajos, duran solo alrededor de 1,500 ciclos con un mantenimiento adecuado, lo que requiere reemplazos cada 2-3 años junto con los costos de eliminación de las unidades antiguas.
Una batería elevadora de iones de litio, por otro lado, es un 55% más ligera que las baterías de plomo-ácido y ofrece beneficios, como requisitos de espacio reducidos, carga más rápida, mayor eficiencia energética, mejor seguridad de los trabajadores, un mejor rendimiento del frío y una mayor productividad.
Conclusión
Las baterías de iones de litio, aunque inicialmente más caras, proporcionan ahorros a largo plazo a través de la eficiencia y el menor mantenimiento. Su rápida carga, durabilidad y seguridad los hacen ideales para las carretillas elevadoras.
Al elegir entre plomo-ácido y iones de litio, considere su frecuencia de uso y necesidades de seguridad. Una inversión de batería inteligente aumenta la productividad y reduce el tiempo de inactividad, lo que ayuda a su empresa a mantenerse competitiva en el mercado de carretillas elevadoras eléctricas.

