À retenir :
- Identifiez la défaillance de la batterie lithium-ion avec des signes tels que des temps de chargement plus longs, une surchauffe et un gonflement. Utilisez des chargeurs de qualité et stockez correctement les batteries pour prolonger la vie.
Le risque de batterie lithium-ion Les accidents ont diminué à mesure que la technologie s'est améliorée. Cependant, des problèmes peuvent encore se produire.
Beaucoup souhaitent identifier les batteries au lithium-ion défectueuses, qui peuvent présenter des symptômes comme une capacité réduite, une basse tension, une auto-décharge rapide, une surchauffe et un gonflement.
Cet article discutera de la façon de vérifier la défaillance de la batterie au lithium-ion.
Causes de défaillance de batterie au lithium-ion
Les batteries au lithium-ion, malgré la protection du BMS, restent vulnérables aux facteurs internes et externes qui peuvent provoquer une défaillance.
Intérieurement, fabrication Des problèmes tels que les prix des prix, les matériaux inférieurs à la Parce et la production bâclée peuvent compromettre la durabilité et les performances.
L'extérieur, les conditions environnementales comme la température, l'humidité, la pression de l'air et le stress physique peuvent avoir un impact négatif sur la santé des batteries au fil du temps.
Signes communs Lithium-Ion Battery échoue
Votre batterie lithium-ion ne durera pas éternellement, mais il y a des signes révélateurs qu'il commence à échouer.
1. Temps de charge plus long
La charge plus lente indique que votre batterie perd une capacité et ne tiendra pas de charge aussi longtemps.
Il s'agit d'un signe précoce que votre batterie lithium-ion échoue, car ces batteries perdent progressivement le stockage et l'efficacité d'énergie au fil du temps.
2. durée de vie de la batterie plus courte
Un taux de décharge rapide est un signe initial de dommage à la batterie au lithium-ion.
Si votre batterie a besoin de recharge fréquente, cela peut indiquer que la batterie s'use et doit être remplacée.
3. Surchauffe
Une chaleur excessive pendant l'utilisation ou la charge de la batterie est une préoccupation.
Une certaine chaleur est normale, mais des augmentations de température anormales pourraient indiquer des problèmes internes.
Surveillez toute augmentation de chaleur notable, car la surchauffe affecte les performances et présente les risques de sécurité.
Une chaleur excessive peut entraîner emballement thermique, où la température continue de monter, ce qui rend l'appareil dangereusement chaud. Cela indique que la batterie a besoin d'inspection plus approfondie.
4. Incapacité à charger
Une batterie morte est un problème courant pour les utilisateurs d'électronique portable.
Lorsqu'un appareil ne se charge pas, il indique probablement une batterie mourante qui doit être remplacée.
5. puissance inattendue
Lorsqu'un appareil s'arrête soudainement malgré une grande durée de vie de la batterie, il indique souvent une batterie lithium-ion défaillante.
Si cela persiste, la batterie doit être remplacée par un professionnel.
6. Indicateur de batterie inexacte
Même avec un compteur de batterie complet, les appareils peuvent mourir de façon inattendue, indiquant une batterie défaillante qui doit être remplacée.
7. Mauvais temps de réponse
Le mauvais temps de réponse de votre appareil peut indiquer une batterie faible ou entraîner des problèmes de surcharge de données ou de logiciels.
8. Basse tension
Les batteries perdent progressivement la tension au fil du temps.
Lorsqu'une certaine tension est détectée, le circuit de coupure déconnecte immédiatement la batterie.
Par exemple, une batterie au lithium-ion de 4,2 V peut passer à 3,7 V après la charge et la décharge répétés.
L'appareil cesse de fonctionner une fois que la batterie tombe en dessous de 3,4 V, et elle est inutilisable à 3. 0V.
9. Fréquence élevée de l'auto-décharge
Les batteries perdent finalement leur charge lorsqu'ils ne sont pas utilisés.
Les batteries au lithium-ion de haute qualité ont un faible taux d'auto-décharge.
Retirez la batterie après deux heures et vérifiez le niveau de charge avant de débrancher.
Si les lectures sont en dehors de la plage spécifiée, supposons que la batterie est cassée.
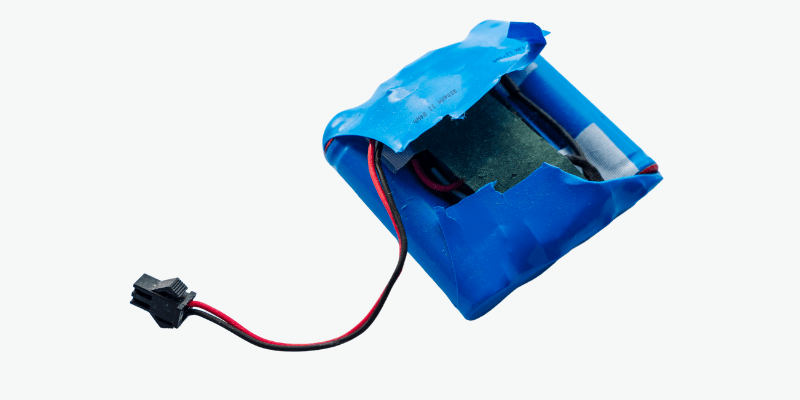
10. gonflement ou renflement
Un gonflement ou un renflement dans le boîtier de la batterie indique des problèmes internes.
Une batterie déformée signale la défaillance potentielle et les risques de sécurité, y compris les fuites ou l'explosion.
Un gonflement se produit en raison de l'accumulation de gaz à partir de la panne ou des dégâts des composants internes, provoquant une augmentation de la batterie.
Dépannage des problèmes de batterie au lithium-ion
Testez immédiatement votre batterie lithium-ion si vous soupçonnez qu'elle fonctionne mal.
Des problèmes comme les incendies peuvent être causés par une batterie défectueuse. Utilisez un multimètre pour tester la batterie.
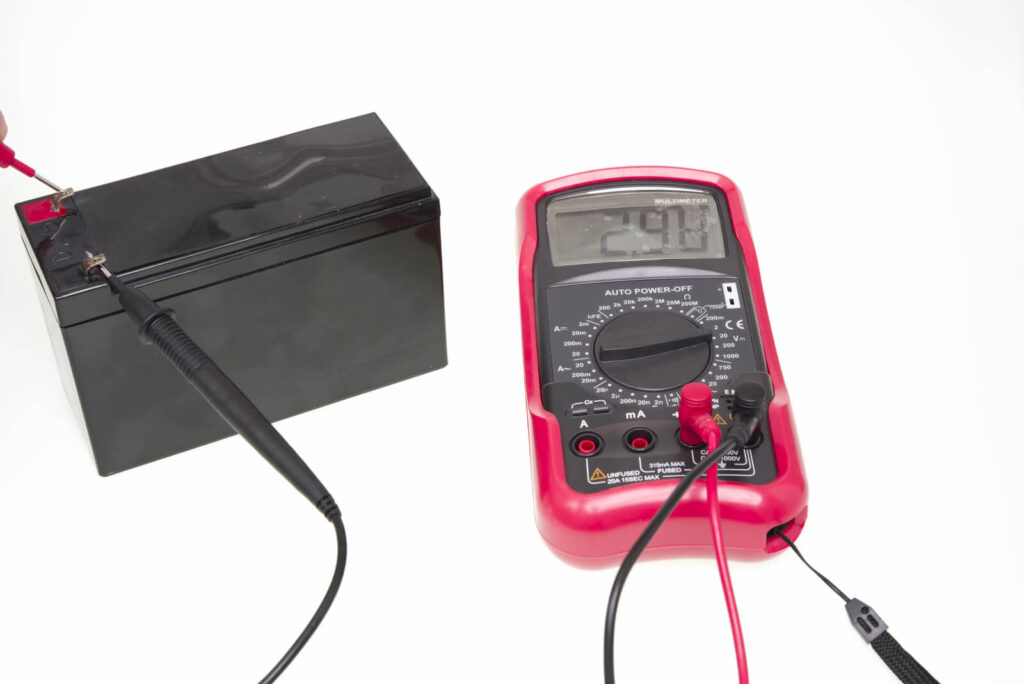

Retirez-le de son boîtier et connectez les entraînements positifs et négatifs du multimètre aux bornes de la batterie. Puissance sur le multimètre et activer “Tension de courant continu” mode. Placez les sondes sur les terminaux et lisez les résultats.
Une batterie lithium-ion endommagée peut montrer une tension en dessous de son niveau normal 3. 7V, comme 3. 5V ou moins.
Vérifiez la capacité de la batterie en déchargeant pleinement et en prenant une nouvelle lecture – Une batterie endommagée aura moins de puissance.
Remplacez la batterie lithium-ion dès que possible si vous soupçonnez des dommages. Cela ne vaut pas le risque de continuer à utiliser une batterie compromise.
6 façons d'étendre la vie des batteries au lithium-ion
1. Utilisez un chargeur de haute qualité conçu pour les batteries au lithium-ion afin d'éviter de réduire la durée de vie des batteries.
2. Évitez la surcharge – Ne laissez pas les batteries charger la nuit sauf si nécessaire.
3. Ne déchargez pas trop les batteries, visez à les garder au-dessus de 50%.
4. Ranger les piles Dans un environnement frais et sec pour prolonger leur durée de vie.
5. Utilisez des batteries de confiance de haute qualité de fabricants connus pour éviter les dommages.
6. Évitez chaleur extrême et froid.
Conclusion
Cet article couvrait les panneaux de défaillance de batterie au lithium-ion communs, comme une charge plus longue, une durée de vie plus courte, une surchauffe et des fermetures inattendues.
Il a également offert des conseils pour prolonger la durée de vie de la batterie, comme l'utilisation de chargeurs de qualité, d'éviter la surcharge et le stockage dans un endroit frais et sec.
Être conscient des problèmes potentiels et prendre des précautions peuvent aider à garantir des performances sûres et fiables des appareils alimentés au lithium-ion.
Articles Liés: