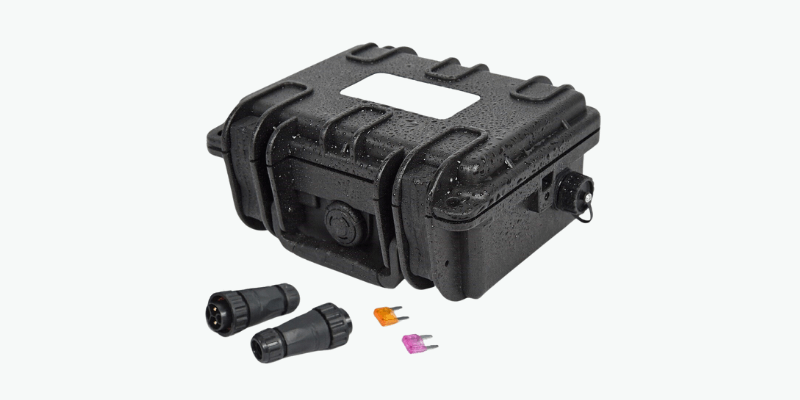
Lithium batteries should never be submerged in water due to the risk of damage. High-quality LiFePO4 batteries, like Holo Battery custom solutions, are designed with extensive sealing and IP65 ratings for moisture resistance. Today, let’s explore whether lithium batteries can get wet.
Lithium Batteries vs. Lead-Acid Batteries
Understanding lithium batteries requires comparing them to lead-acid batteries.
Lead-Acid Batteries
These consist of two lead plates – a positively charged cathode and a negatively charged anode, submerged in sulfuric acid. When power is drawn, sulfate ions move to the negative plate, releasing electrons for electricity. During charging, this process reverses. Distilled water must be regularly added to maintain electrolyte balance.
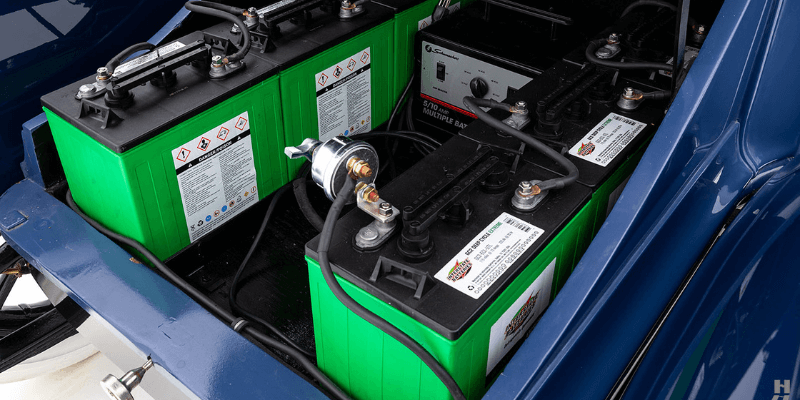
Lithium Batteries
Similar to lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries allow lithium ions to travel through the electrolyte and release electrons when energy is drawn; this also reverses during charging.
However, they are sealed and require no maintenance or access for balancing electrolytes. This design protects internal components and increases safety compared to lead-acid batteries.
Can Lithium Batteries Get Wet?
The short answer is sometimes, depending on the battery quality and design.
Holo Battery’s custom marine batteries are fully sealed and IP65 rated, making them water-resistant. They perform well in moist environments, but prolonged exposure to high moisture can cause irreversible damage.
For other lithium-ion batteries, check the manufacturer’s water exposure specifications. While most lithium batteries are sealed cells with some water protection, not all seals are equal.
Generally, lithium batteries can withstand rain or splashing but may require additional precautions based on manufacturer recommendations.
Regardless of their water resistance levels, no lithium battery should be submerged in water, as it can severely damage performance or render them inoperable.

What Happens When Lithium Batteries Get Wet?
Typically, the answer is nothing!
The sealed design of Holo Battery lithium batteries protects critical components from occasional water exposure.
However, prolonged contact can damage sensitive components like battery terminals. Water inside the battery can trigger hazardous chemical reactions and create current pathways between terminals, leading to unintentional discharge.
How Does Salt Water Impact a Lithium Battery?
Exposure to salt water can harm lithium batteries in several ways:
- Corrosion: Salt water corrodes battery terminals and metallic components, reducing electrical conductivity and performance.
- Short circuits: As a good conductor, salt water can cause short circuits if it enters the battery casing, leading to overheating, leakage, or fire.
- Chemical reactions: Salt water may trigger harmful chemical reactions within the battery that accelerate component degradation.
- Reduced lifespan: Prolonged exposure significantly shortens a lithium battery’s lifespan due to corrosion and internal damage.
Can You Recharge Wet Lithium Batteries?
Keep your battery dry. Minimal water or a moist environment won’t affect recharging, but avoid recharging if the battery is submerged in water. If you suspect water damage to your lithium battery, do not recharge it. Instead, dispose of it safely.
Can You Leave Lithium Batteries Outside?
Lithium batteries are sealed, posing no danger when left outside.
LiFePO4 batteries can operate in various temperatures, allowing them to function in different weather conditions. Thus, occasional outdoor use shouldn’t damage them.
However, avoid exposing lithium batteries to the elements for extended periods. Protecting them from rain, wind, water, and extreme temperatures will extend their lifespan and save you money and hassle in the long run.
What Precautions Should I Take to Keep My Lithium Batteries From Getting Wet?
To protect your lithium batteries from moisture, consider these precautions:
- Storage: Keep batteries in a dry, secure location away from water exposure.
- Sealing: Ensure battery compartments are properly sealed to prevent water ingress.
- Protection: Use waterproof cases when carrying or storing batteries in moist environments.
- Avoid submersion: Never submerge lithium batteries in water or expose them to excessive moisture.
- Regular checks: Periodically inspect enclosures and seals for wear or damage that may compromise waterproofing.
By following these steps, you can maintain the integrity and functionality of your lithium batteries.
What is an IP65 Rating?
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings assess the quality of enclosures around electronic devices, indicating their effectiveness against foreign objects and moisture. IP ratings use a two-digit scale: the first digit (0-6) measures intrusion protection, while the second digit (0-9) measures moisture protection.
Our custom lithium batteries have an IP65 rating, meaning they are “totally dust tight” and water-resistant against 6.3mm low-pressure jets from any angle. This ensures our batteries remain secure in moderately moist environments or when exposed to small amounts of water, as these levels cannot penetrate their protective sealing.
How to Waterproof Your Batteries
If your lithium batteries will be exposed to moisture, consider waterproofing them. Secure, dry-box-style compartments and tightly wrapping or coating batteries in materials like urethane coatings, silicone, or rubberized paints can provide extra protection, as long as the terminals remain accessible.
Pro Tip: Use a battery box to keep batteries warm and dry. These containers protect against water and hazards during transport. They often have ports for drawing power and charging without removal, giving ice fishermen peace of mind in extreme conditions.
How Safe Are Lithium Batteries on a Boat?
Lithium marine batteries are very safe for use on the water with basic care. They are ideal for those needing extensive storage, quick charging, and reliable performance in various conditions.
Compared to lead-acid batteries, lithium options offer more flexible mounting and reduced hazard risk in rough seas.
Fully sealed lithium batteries have a lower chance of water-related damage, with lithium-iron phosphate (LiFePO4) being particularly safe and stable against thermal runaway.
Don’t Panic If Your Lithium Batteries Get Wet
Don’t Worry If Your Lithium Batteries Get Wet
Lithium batteries can get wet. Thanks to their sealed design, they can withstand direct contact with water without severe or lasting damage. While extended water exposure can be harmful, taking proper precautions will ensure your batteries remain operational.

