In the world of energy storage, lithium-based batteries are essential for powering everything from gadgets to electric cars. There are two main types: lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries. Although both use lithium, they differ significantly in construction, performance, applications, and safety. Let’s explore what sets them apart!
What is A Lithium-metal Battery?
A lithium-metal battery uses metallic lithium for its anode, allowing it to pack a lot of energy into a small space. When charged, lithium ions move to the anode and form metallic lithium. When the battery is in use, these ions return to the cathode, releasing energy in the process.
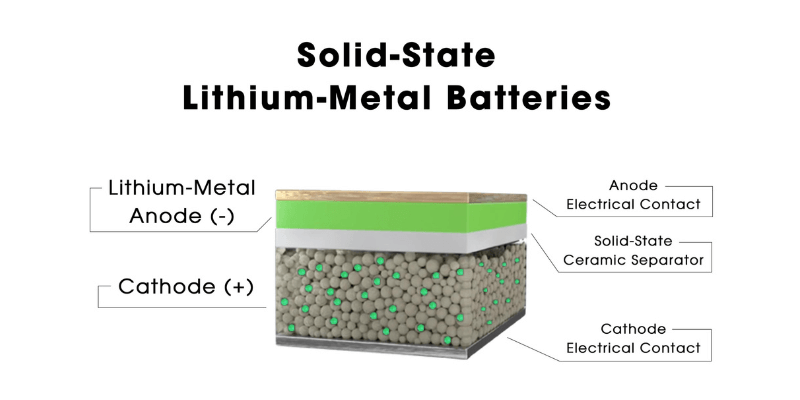
Lithium-metal Battery Advantages
Lithium-metal batteries provide key advantages as below:
- Higher energy density: Lithium-metal batteries can store more energy in less space, potentially resulting in longer-lasting devices and greater range for electric vehicles.
- Lighter weight: Their lightweight design makes them ideal for portable applications like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, reducing overall device weight.
- Faster charging: Lithium-metal batteries allow for quicker charging, replenishing battery power in less time.

Lithium-metal Battery Limitations
Lithium-metal batteries also come with significant limitations that need to be addressed:
- Safety Concerns: Dendrites can form from the lithium metal anode, piercing the separator and causing short circuits, overheating, or fires.
- Limited Cycle Life: Lithium-metal batteries have a shorter cycle life than lithium-ion batteries due to dendrite formation that damages capacity over time.
- Manufacturing Challenges: Producing lithium-metal batteries is more complex and costly than lithium-ion production due to lithium’s reactivity requiring specialized handling.
- Environmental Sensitivity: These batteries are sensitive to temperature variations and need precise control of operating conditions for optimal performance and safety.
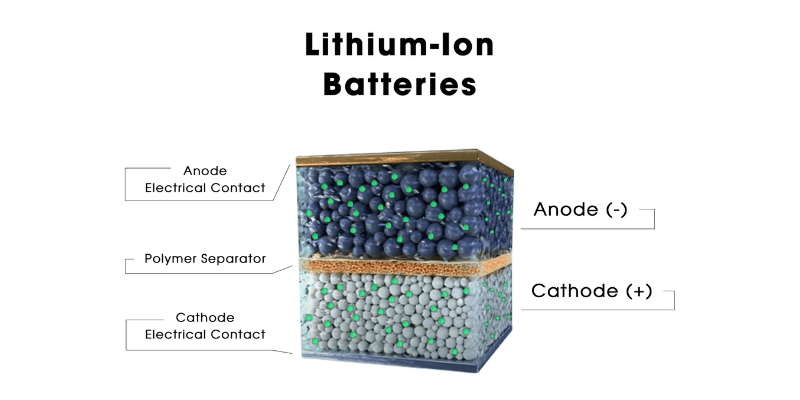
What is A Lithium-ion Battery?
Lithium-ion batteries use carbon materials like graphite for their anode. The main components of these batteries are the cathode, anode, separator, and electrolyte. When charged, lithium ions travel from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte and stay there. Then, when you use your device, they return to the cathode, creating electrical energy to power it.
Lithium-ion Battery Advantages
Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their impressive advantages:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries deliver significant power in a small space, allowing devices to be smaller and lighter while maintaining long battery life.
- Rechargeable: Unlike disposable batteries, lithium-ion batteries can be recharged repeatedly, saving money and reducing waste.
- No Memory Effect: Unlike older batteries that needed complete discharges before recharging or risk losing capacity, lithium-ion batteries can be charged at any time without affecting lifespan.
- Low Self-Discharge: These batteries lose less charge over time when not in use, holding their charge longer.
- Variety of Applications: Lithium-ion batteries are versatile and used in many devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles.

Lithium-ion Battery Limitations
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used but have limitations:
- Cost: Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive to produce than older battery types. This higher cost may impact the affordability of devices that rely on them.
- Limited Lifespan: Although rechargeable, their charge-holding ability declines over time, requiring replacement due to internal chemical changes.
- Safety Concerns: Damaged or overheated lithium-ion batteries can pose fire risks and lead to “thermal runaway,” potentially causing fires or explosions. Following manufacturer instructions for charging and storage is crucial.
- Environmental Impact: Mining lithium and other materials has negative effects on the environment, and proper disposal is needed to prevent pollution.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Extreme temperatures can impact performance and lifespan; they work best within a specific temperature range.

Key Differences Between Lithium-ion Battery And Lithium-metal Battery
Here’s a summary of the key differences between lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries:
Anode Material
- Lithium-ion: Uses graphite as the anode, intercalating lithium ions within its structure.
- Lithium-metal: Utilizes pure metallic lithium, allowing for higher ion storage capacity.
Energy Density
- Lithium-ion: Good energy density but limited by the carbon-based anode’s capacity.
- Lithium-metal: Much higher energy density enables longer-lasting devices and greater electric vehicle range.
Rechargeability
- Lithium-ion: Rechargeable, allowing repeated use.
- Lithium-metal: Most are non-rechargeable, but research is ongoing to make them rechargeable.
Safety
- Lithium-ion: Generally safe but can pose fire risks if damaged or misused.
- Lithium-metal: Higher safety risks due to dendrite formation that can cause short circuits and fires.
Cycle Life
- Lithium-ion: Good cycle life, lasting hundreds or thousands of charges before degradation.
- Lithium-metal: Shorter cycle life due to irreversible damage from dendrites during charging/discharging.
Commercial Availability
- Lithium-ion: Mature technology widely available across devices.
- Lithium-metal: Mostly in research stages; safety and cycle life challenges hinder commercialization.
Cost:
- Lithion-ion: Lower production costs due to matured technology.
- Lition-metal: More expensive because of manufacturing complexities and lower volumes.
Conclusion
Lithium-metal batteries pack more energy, but they face safety and lifespan issues due to dendrite formation. Before they can replace lithium-ion batteries, these challenges need to be resolved. Fortunately, researchers are diligently working to address these problems.