Ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela ixhaphakile, kodwa ayifanelanga ihoyiwe. I-terminals ehleliweyo inokunciphisa ubomi bebhetri kwaye ibangele imiba yombane. Kwezi sikhokelo, siza kuphonononga indlela yokuthintela kunye nokucoca i-corosion yebhetri xa yenzekile.
Ithini i-terrosion yebhetri?
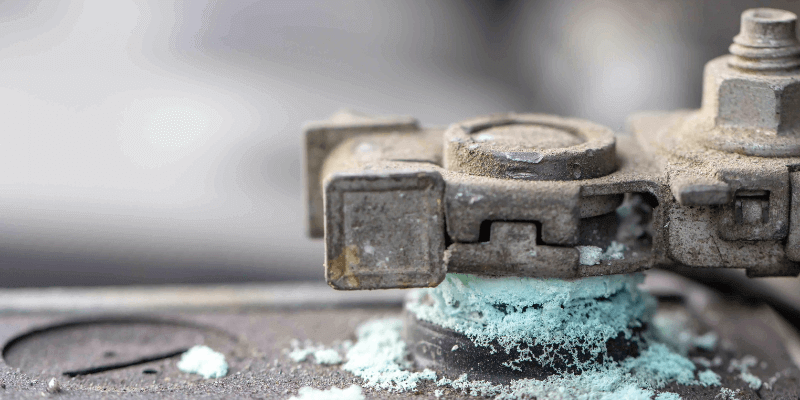
Ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela ye-Prerasion yenzeka xa igesi ye-hydrogen evela kwibhetri ye-acid enomoya, ukufuma kunye netyuwa.
Kulula ukubona: Khangela i-mhlophe, iblue, okanye i-green i-green ejikeleze i iitheminali zebhetri, iiposti, okanye iintambo. Lo mgubo unesimo segranular.
YINTONI EBALULEKILEYO IXESHA LOKUGQIBELA?
Kukho izizathu ezahlukeneyo zokupheliswa kwetekisi. Umzekelo, ukongeza amanzi amaninzi ngexesha lolondolozo kunokubangela i-acid yebhetri yokubaleka, kwaye igqithise ngaphezulu kuchaphazela isiphelo sendlela efanelekileyo. Nakuphi na ukuvezwa kwezinto zebhetri kwizinto ezisebenzayo, kubandakanya nemozulu embi, inokukhokelela ekusuleni. Esi simo sengqondo sibonisa ukukhutshwa kwegesi eyingozi kwiibhetri.
Okuchasene, Iibhetri ezikumgangatho ophezulu zeLithium Njengomgca webhetri ye-holo ye-holo ayikhupheli igesi kunye nokuxhathisa i-terrosion yesiphelo, esenza ukuba bakhuseleke kunemveli Iibhetri ze-acid.
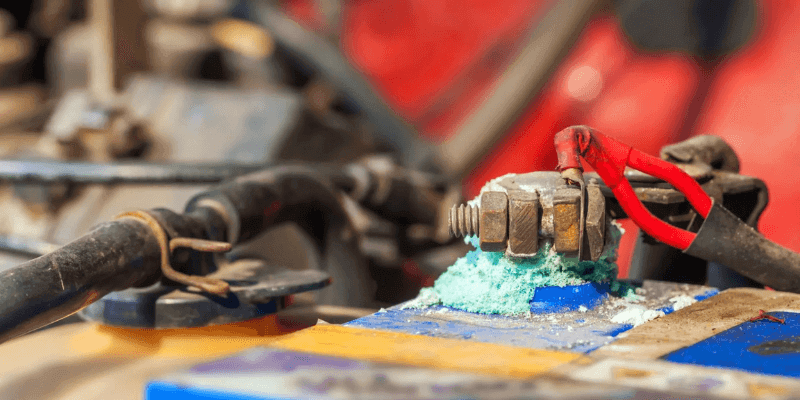

Kwenzeka ntoni ukuba ii-terrode zebhetri?
Ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela yokususwa kwebhetri iphakamisa i-Pounds kwibhetri ukuya kwisixhobo, okukhokelela ekunciphiseni kwamandla. Kwiimeko ezinzima, ucoceko lungathintela ibhetri ukuba ibonelele ngamandla awoneleyo ezixhobo okanye izithuthi ukuba ziqale.
Ukuzoba okuphezulu ngoku kwizikhululo eziqhotyoshelweyo kunokubangela ukugxeka, iintambo ezonakalisayo kunye neebhetri ngenxa yokungaxhathisi kunxibelelwano.
Ngaba ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela ibonisa ibhetri embi?
Akunjalo. Ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela inokubonisa ukuba ibhetri yakho iyasilela, ngakumbi kwiibhetri ezindala. Nangona kunjalo, impazamo yomsebenzisi inokuba negalelo nakwiimeko ezithile.
I-South kuyinto eqhelekileyo kwiibhetri ze-acid ezisetyenziselwa ukuhamba ngebhayisikile enzulu, njengakwi-RVS, iinqanawa, okanye iinkqubo zegridi, ngenxa yokukhutshwa kwegesi ngexesha lokucocwa kwexesha elide. Ngenxa yoko, iibhetri ze-acid azifanelekanga ukuba zihambele phambili ukuhamba ngenyawo; Iibhetri zeLithium zizikhetho eziphezulu nezikhuselekileyo.
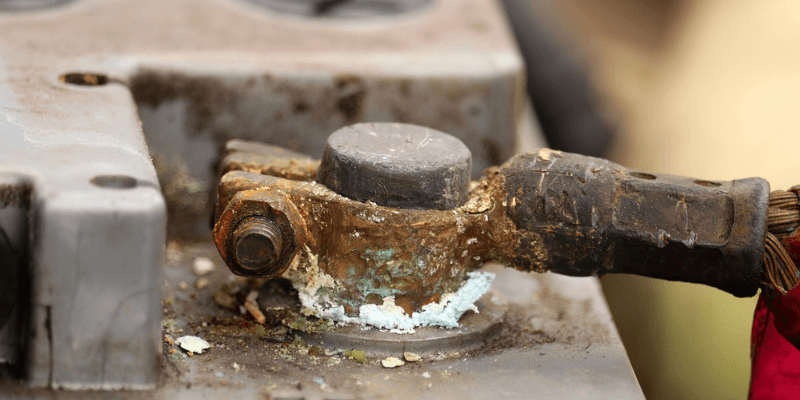

Ngaba ibhetri yesiphelo sendlela yokuphelisa i-Electronics?
Ibhetri encinci ye-acid ifuna kuphela ukucocwa okanye ukutshintshwa kwesiphelo, kodwa ukuvuza okukhulu kunokwenzakalisa i-elektroniki ebuthathaka. Ukuthintela ukuvela kwebhetri kwizixhobo ezixabisa kakhulu okanye ezibuthathaka kakhulu kubalulekile.
Ukuba usebenzisa iibhetri ezikhokelayo-acid, qinisekisa ukuba bangena ngaphakathi kwaye bade kwizinto ze-elektroniki.
Indlela yokucoca i-Plates yeThebhu yebhetri
Ukhuseleko kuqala
Ngaphambi kokuqala, khumbula ukuba i-corosion yebhetri yi-caustic. Hlala unxibe iigloves ezinzima kunye nokukhuseleka kwamehlo ukuthintela ukucaphukisa. Hlambulula nayiphi na indawo echaphazelekayo emanzini kwangoko.
Hlula ibhetri
- Nqamla i-terminal engalunganga kuqala, emva koko, emva koko. Sebenzisa imemori yememori yebhetri ukukhusela inkqubo yombane wakho ngexesha lokunqunyanyiswa okwandisiweyo.
- Vavanya iintambo zokutshiza, ukukhupha, okanye ukufakelwa okuphambili, kwaye ubeke endaweni yazo nawaphi na amalungu owonakalisiweyo.
Ukususa kunye nokucoca ibhetri
- Ukucocwa okukhuselekileyo, susa ibhetri yemoto kwaye ubeke kwipani engaxinanga ukuze ubambe umkhuhlane.
- Sebenzisa ibrashi ye-wire okanye i-scraper ukususa i-corrosion kunye nobumdaka kwizikhululo kunye nebhetri.
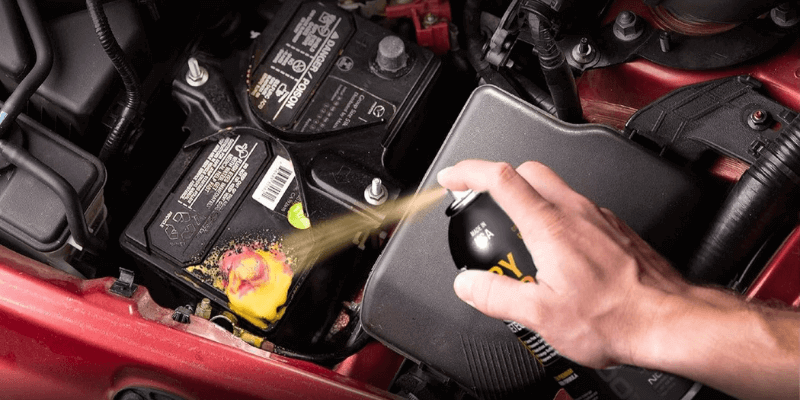
- Sebenzisa ibhetri yesiphelo setekisi ukuze ususe i-corosion.
- Hlanganisa isoda yokubhaka ngamanzi afudumeleyo ukwenza isisombululo sokungathathi cala. Dipha i-rag kwisisombululo kwaye usule ukuvela. Kulumkele ukuthulula ngokuthe ngqo kwibhetri ukukhusela iiseli zangaphakathi.
Ukugqiba ukuchukumisa
- Sebenzisa ilaphu le-microfiber ukomisa ibhetri, iziphelo kunye neentambo. Coca iziphelo ngebrashi ukususa inkunkuma.
- Ibhetri kwakhona, ukuqala nge-terminal elungileyo elandelwa nguwe. Khusela i-downs-downs.
Thintela i-tarrosion yesiphelo sendlela yokutshintsha kwi-lithium
Eyona ndlela ilula yokuthintela i-corosion yebhetri kukusebenzisa iibhetri ze-lithium, engacacanga. Itekhnoloji yale mihla inika izibonelelo ezininzi kwabo batshintsha.
Akukho fuduidic
I-Lithium Barters yahlukile kwi-Over Uyilo lwabo olutywiniweyo lususe imfuneko yokukhupha nayiphi na impundu.
Akukho londolozo
Iibhetri ezikhuthazayo ezisemgangathweni zifuna ukulondolozwa rhoqo, njengokuthoba rhoqo kwiiveki ezimbalwa okanye iinyanga.
Ngokwahlukileyo, iibhetri ze-lithium-ion akufuneki zilondolozo ngobunini; Xa sele ifakiwe, zibekekile izandla ekutshatweni.
Izibonelelo ezingakumbi
Iibhetri zeLithium zibonelela ngaphezulu kokhuseleko lokungasebenzi kwaye akukho londolozo. Zihlala ixesha elide kwiibhetri zemveli, ukunciphisa imvaphulelo. Bakhanya kunebhetri ye-Acid-Acid, abavumela abasebenzisi ukuba basike ubunzima okanye ukonyusa amandla ngaphandle kongeza ubunzima.
Ukongeza, baqhuba kakuhle kubushushu obukhulu kwaye banokukhutshelwa ngakumbi, ukujongana nemicimbi emibini ephambili ngebhetri.
Ukuqukumbela
I-Colososion inokuba malunga, ngakumbi malunga neebhetri kunye nomngcipheko wokuvezwa kwe-acid yebhetri.
Nangona kunjalo, ngokulandela esi sikhokelo, unokukuphepha uninzi lwe-terrosion yebhetri kwaye ichaphazele ngokufanelekileyo ukuba iyenzeka. Ukutshintshela kwiibhetri ze-lithium zanamhlanje kunokuphelisa ukukhathazeka malunga ne-corosion yebhetri ngokupheleleyo.


