Batterien führen alles an, von Telefonen bis hin zu Autos, was sie im täglichen Leben wesentlich macht. Die Batterieleistung variiert jedoch. Das Verständnis der Spannung ist bei der Auswahl zwischen verschiedenen Batterien von entscheidender Bedeutung. Lassen Sie uns untersuchen, was Spannung ist, wie man sie misst und welche chemischen Reaktionen beteiligt sind.
Was ist Batteriespannung?
Die Batteriespannung ist die Differenz des elektrischen Potentials zwischen den positiven und negativen Klemmen einer Batterie. Es repräsentiert den Druck, der Elektronen von einem Punkt zum anderen drückt.
Sie können sich dies als komprimierte Feder innerhalb der Batterie vorstellen, wo eine größere Kompression mit erhöhter potentieller Energie korreliert, wenn sie freigesetzt werden. Dieses Merkmal ist für die Bestimmung der Leistung einer Batterie, die erforderliche Spannung für Geräte und den Ladungszustand von wesentlicher Bedeutung.
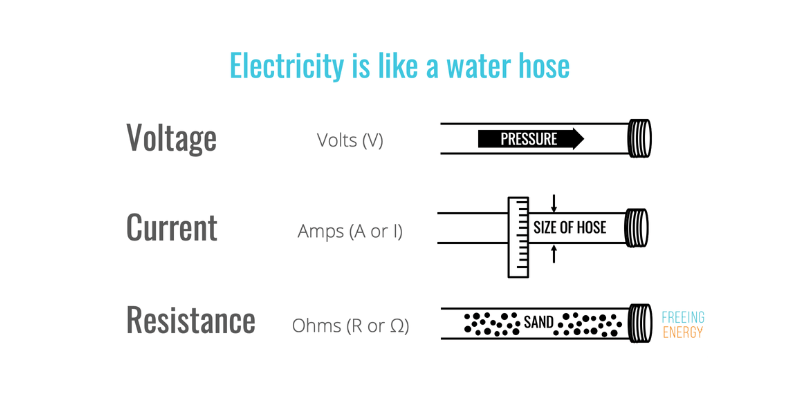
Eine weitere Analogie ist der Wasserdruck in einem Schlauch: Spannung drückt Wasser durch den Schlauch (Strom), gemessen in Verstärker. Unterschiedliche elektrische Systeme erfordern unterschiedliche Spannungen: 12-48 Volt für niedrige Gleichstromsysteme bis 110 V oder 220 V für Wechselstromanwendungen. Höhere Spannungen drücken mehr Strom durch Drähte; Überlegen Sie, wie kraftvoll ein Hochdruckwasserstrom sein kann.
Während niedrigere Spannungen (unter 50 Volt) nach OSHA -Standards im Allgemeinen sicher sind, können elektrische Ströme bei höheren Spannungen in Wohnwerten und Stromleitungen gefährlich sein.

Was erzeugt Batteriespannung?
Batterien bestehen aus einem Anode, Kathode, Elektrolytund Trennzeichen. Die Anode ist die negative Seite, typischerweise aus Zink, Lithium, Graphit oder Platin. Die Kathode ist das positive Ende und enthält normalerweise oxidierende Metalle wie Lithiumoxid oder Kupferoxid.
Elektronen können nicht frei zwischen Anode und Kathode fließen; Wenn sie jedoch von einem Leiter verbunden sind, bewegen sich die Elektronen von der Anode zur Kathode und erzeugen Spannung.

Was ist der Unterschied zwischen Spannung und Strom?
Spannung und Strom sind eng miteinander verbunden und haben jedoch unterschiedliche Eigenschaften.
- Die Spannung misst die elektrische Potentialergie pro Ladung der Einheit, während der Strom die Elektronenströmungsrate darstellt.
- Die Spannung wird in Volt (V) und Strom in Ampere (a) gemessen.
- Spannung, gekennzeichnet durch “V,” treibt Strom innerhalb einer Schaltung an, während der Strom bezeichnet wird durch “ICH,” bedeutet den Elektronenfluss.
- Die Spannung wird als unabhängig von der Schaltung angesehen, während der Strom durch den Widerstand des Schaltkreises beeinflusst wird.
Wie wird die Batteriespannung gemessen?
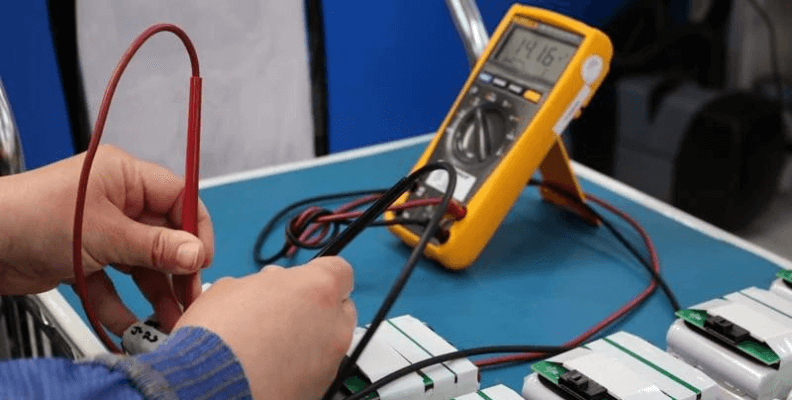
Die Messung der Batteriespannung ist für die Bestimmung des Ladungszustands unerlässlich.
Die beste Methode besteht darin, einen Multimeter zu verwenden: Befestigen Sie die rote Sonde an das positive Anschluss und die schwarze Sonde am negativen Anschluss und nehmen Sie dann den Messwert.

Was ist normale Spannung?
Die normale Spannung einer Batterie hängt von ihrer Art und chemischen Reaktion ab. Batterien mit günstigeren Oxidationsreduzierungsreaktionen erzeugen höhere Spannungen. Beispielsweise misst eine Autokatterie in der Regel etwa 12,6 Volt, während eine AAA -Batterie etwa 1,5 Volt misst.
Es ist entscheidend, der richtigen Spannung zu entsprechen, um eine schädliche Elektronik oder die Batterie zu vermeiden.
Blei-Säure-Spannungen gegen Lithium-Ionen-Batteriespannungen
Die Batteriespannung variiert mit dem Ladungspegel. Eine voll aufgeladene Batterie liefert eine höhere Spannung als eine, die niedrig oder leer ist. Dieses Phänomen, das als Spannungsverlust bezeichnet wird, hängt vom Batterietyp ab.
Herkömmliche Blei-Säure-Batterien erleben größere Spannungsabfälle als Lithiumbatterien. Lithiumbatterien mit ihrer fortschrittlichen Technologie sind energiedichter und von weniger betroffen von Peukerts Gesetz.
Eine 12-Volt-Blei-Säure-Batterie liefert bei voll geladenem und 11,6 Volt bei 20% Kapazität etwa 12,7 Volt. Im Vergleich dazu liefert eine Lithiumbatterie 13,6 Volt, wenn sie vollständig aufgeladen ist und 12,9 Volt bei 20% Kapazität.
Ist die Batteriespannung gefährlich?
Entsprechend OSHADie Batteriespannung wird nicht als gefährlich angesehen, wenn sie 50 Volt überschreitet. Der menschliche Körper kann im Allgemeinen ohne Schaden bis zu 50 Volt Schock standhalten, da die Arme und Beine einen Widerstand von mindestens 500 Ohm haben. Dieser Widerstand verhindert, dass tödlicher Strom in den meisten Fällen das Herz erreicht.
Spannungen über 50 Volt können den Körper jedoch zu einem Leiter machen und ernsthafte Risiken darstellen, einschließlich Verbrennungen, Knochenbrüche, Hörverlust, Augenverletzungen, Herzstillstand und Tod. Sogar 10 Milliamps durch das Herz können seine elektrische Leitfähigkeit stören und tödliche Arrhythmien verursachen. Somit gelten alle Spannungen über 50 Volt als gefährlich.
Warum ist Batteriespannung wichtig?
Die Batteriespannung ist wichtig, da sie angibt, wie viel Strom eine Batterie liefern kann, um die erforderliche Spannung für die Elektronik und ihren Ladungszustand zu bestimmen. Ohne die Batteriespannung zu messen, wäre sicher unmöglich, wenn Sie Batterien verwenden.