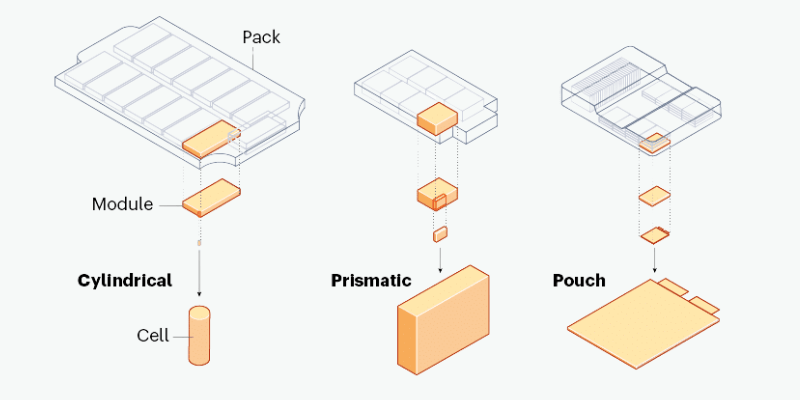
Inzicht in het onderscheid tussen batterijcellen, modules en pakketten is cruciaal voor het ontwerpen van efficiënte energieopslagsystemen. Dit artikel onderzoekt hun constructie, prestatiekenmerken en toepassingen.
Batterijcel
Wat is een batterijcel?
Een batterijcel is de basiseenheid van een batterij, die dient als een kleine container die elektrische energie opslaat en afgeeft door chemische reacties. Het bestaat uit elektroden (anode en kathode) gescheiden door een elektrolyt en ingesloten in een behuizing. Meerdere cellen kunnen worden gecombineerd om een grotere batterij te vormen met een hogere spanning of capaciteit.
Batterijcelontwerp
Maat
Batterijcellen variëren van kleine in elektronica tot grote cellen in elektrische voertuigen, beïnvloeding van de capaciteit en energiedichtheid voor specifieke toepassingen.
Vorm
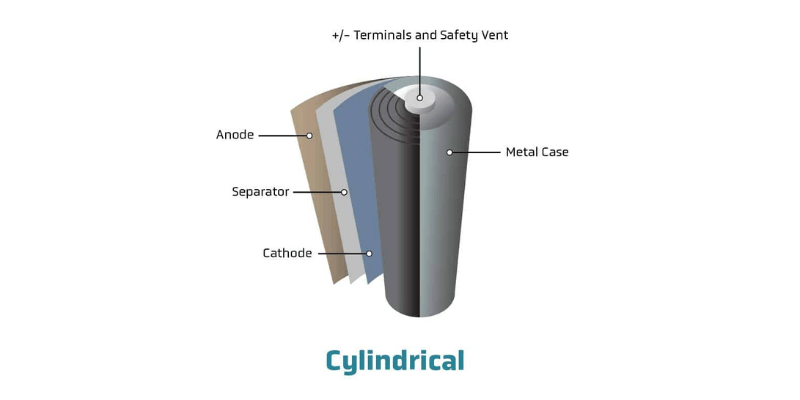
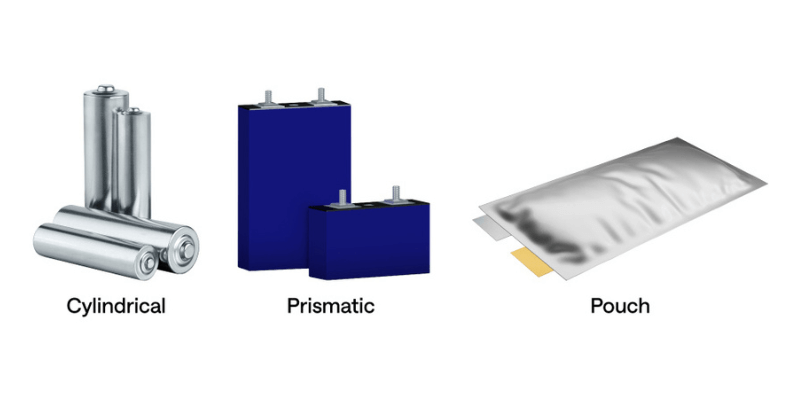
Batterijcellen komen binnen cilindrisch, prismatischen zakontwerpen.
Cilindrische cellen:
- Voordelen: robuuste, consistente prestaties, hoge energiedichtheid.
- Nadelen: lagere specifieke energiedichtheid dan sommige formaten.
- Toepassingen: laptops, elektrisch gereedschap, draagbare consumentenelektronica
Zakcellen:
- Voordelen: hoge energiedichtheid, flexibel ontwerp, kosteneffectief.
- Nadelen: het risico op zwelling, vereist zorgvuldig thermisch beheer.
- Toepassingen: smartphones, tablets
Prismatische cellen:
- Voordelen: hoge energiedichtheid, efficiënt thermisch beheer, schaalbaar ontwerp.
- Nadelen: minder flexibiliteit dan zakcellen.
- Toepassingen: elektrische voertuigen, energieopslagsystemen, industriële toepassingen.
Interne chemie
De interne chemie van een batterijcel bepaalt zijn prestaties, inclusief spanning, capaciteit, en cyclus leven. Verschillende chemie, zoals lithium-ion, nikkel-metaalhydride en loodzuur, bieden verschillende afwegingen in energiedichtheid, kosten en veiligheid. Lithium-ion is bijvoorbeeld de voorkeur vanwege zijn hoge energiedichtheid in draagbare apparaten.
Elektrode materialen
Elektrode -materialen beïnvloeden de prestaties van de batterijcellen en de levensduur aanzienlijk. Gemeenschappelijke opties zijn onder meer lithiumcobaltoxide (liCOO2), lithiumijzerfosfaat (LIFEPO4) en nikkelmanganese kobaltoxide (NMC). Elk biedt verschillende energiedichtheid, stabiliteit en veiligheidsprofielen afgestemd op specifieke behoeften.
Verpakking en inkapseling
Batterijcellen zijn ondergebracht in beschermende verpakkingen om schade door omgevingsfactoren te voorkomen. De verpakking moet isolatie bieden om lekkage van elektrolyt te voorkomen en tegelijkertijd de betrouwbaarheid op lange termijn te waarborgen; Een goede inkapseling gaat ook in op risico's zoals thermische vluchteling of kortsluiting.
Gewoon verpakkingsmaterialen zijn onder meer:
- Metaalblikken: deze beschermen cilindrische cellen en voorkomen kortsluiting.
- Aluminium zakjes: ze bieden een flexibele, lichtgewicht behuizing voor zakcellen.
- Metaalomasten: deze beveiligingsprismatische cellen en hulp bij thermisch beheer.
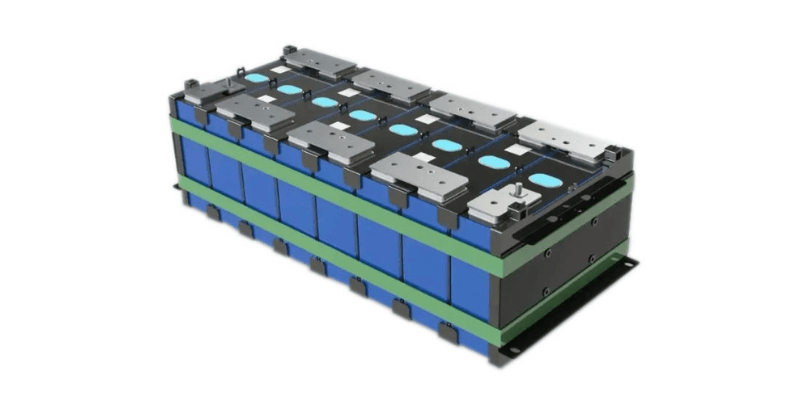
Batterijmodule
Wat is een batterijmodule?
Een batterijmodule bestaat uit verbonden batterijcellen in één behuizing. Het verhoogt de spanning en het capaciteit van een batterijsysteem en dient als een verband tussen individuele cellen en de hele batterij.
Ontwerp van de batterijmodule
Grootte en vorm
De grootte en vorm van de batterijmodule variëren op basis van toepassing en de gewenste energie -uitgang. Gemeenschappelijke configuraties omvatten:
- Pouch-type modules: flexibel en lichtgewicht, gebruikt in consumentenelektronica en elektrische voertuigen.
- Prismatische modules: rigide en stapelbaar, vaak aangetroffen in Elektrische voertuigen en energieopslagsystemen.
- Cilindrische modules: gemaakt van cilindrische cellen, die een hoge energiedichtheid en mechanische robuustheid bieden.
Interne chemie- en elektrodenmaterialen
De chemie en materialen van batterijcellen hebben invloed op de algehele prestaties. Belangrijke factoren zijn onder meer:
- Anodematerialen: gemeenschappelijke opties zijn grafiet-, silicium- en lithiumtitanaatoxide (LTO), die elk unieke voordelen bieden.
- Kathodematerialen: lithium kobaltoxide (LCO), lithiummangaanoxide (LMO), lithiumijzerfosfaat (LFP) en nikkel-cobalt-aluminiumoxide (NCA) verschillen in energiedichtheid, vermogensdichtheid en cyclusleven.
- Elektrolyt: meestal een vloeistof of vaste stof die ionenbeweging tussen de anode en de kathode vergemakkelijkt.
Verpakking en inkapseling
De verpakking van de module beschermt interne componenten en zorgt voor veiligheid. Belangrijkste overwegingen zijn:
- Modulebehuizing: het moet sterk, chemisch resistent en thermisch geleidend zijn.
- Celinterconnectie: betrouwbare bedradingstechnieken zijn essentieel voor celverbindingen.
- Thermisch beheer: voorkomt oververhitting met behulp van koellichamen of faseveranderingsmaterialen.
- Veiligheidsvoorzieningen: neem zekerzakken, stroomonderbrekers of drukontlastingskleppen op om risico's te verminderen.
Batterijbeheersysteem (BMS)
A BMS is een must voor het bewaken van parameters zoals:
- Celspanning: zorgt ervoor dat zelfs opladen en ontladen over cellen.
- Celtemperatuur: voorkomt oververhitting of overmatige koeling.
- Staat van kosten (SOC): volgt de resterende capaciteit.
- Staat van gezondheid (SOH): schat de levensduur van de batterij.
Batterij
Wat is een batterij?
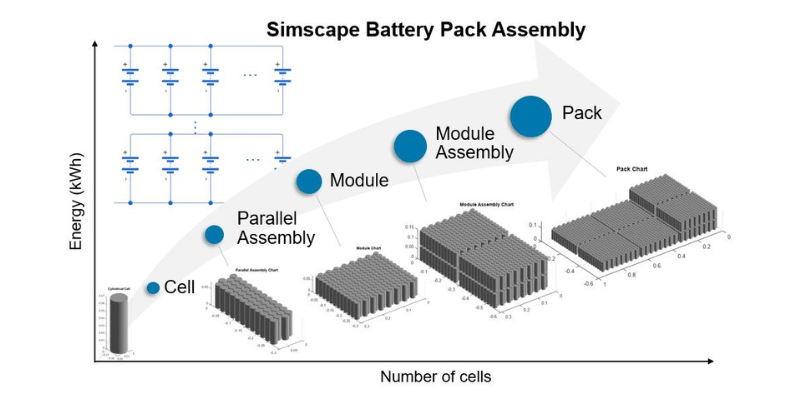
Een batterij bestaat uit batterijcellen of modules die zijn aangesloten om een enkele stroombron te vormen. Cellen zijn gerangschikt in serie en parallel om de gewenste spanning en stroom te bereiken. Batterijpakketten kunnen één cel of duizenden bevatten.
Ontwerp van batterijpakket
Batterijcelopstelling:
- Bepaal de vereiste spanning en capaciteit.
- Selecteer het batterijceltype en de grootte (bijv. Lithium-ion, lithium-polymeer) op basis van prestatiebehoeften.
- Bepaal serie en parallelle configuraties om de gewenste spanning en capaciteit te bereiken.
- Zorg voor uniformiteit in celspecificaties om het evenwicht te behouden.
Woningontwerp:
- Kies materialen voor de batterij die zorgen voor sterkte, duurzaamheid en effectief thermisch beheer.
- Ontwerp de behuizing voor batterijcellen efficiënt. Neem koelopeningen, koellichamen of isolatie op voor temperatuurregulering.
- Bescherm de cellen tegen fysieke schade en omgevingsfactoren zoals vocht en stof.
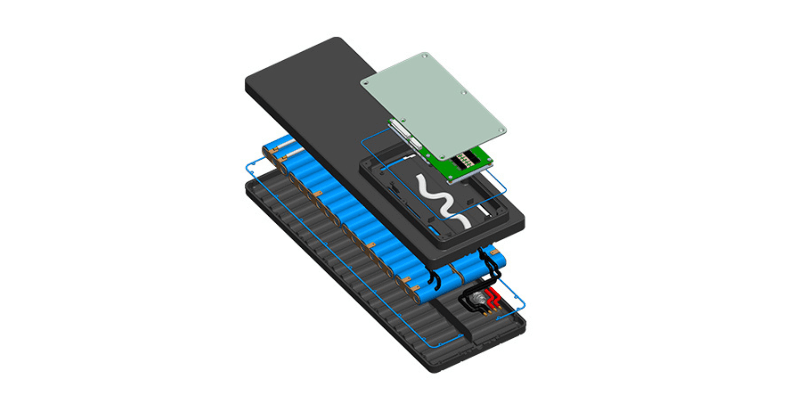
Veiligheidsvoorzieningen:
- Integratie van een BMS om opladen, ontladen en temperatuur te controleren.
- Neem beschermingen op voor overladen, overdekte, kortsluiting en thermische wegloper.
- Installeer zekeringen of stroomonderbrekers voor noodisolatie.
- Zorg voor naleving van VN/DOT -voorschriften en UL -certificeringen.
Elektrische verbindingen:
- Ontwerp elektrische verbindingen met lage weerstand tussen cellen/modules/terminals Om energieverlies te minimaliseren.
- Gebruik hoogwaardige materialen voor betrouwbare verbindingen die spanningsdruppels of fouten verminderen.
- Implementeer isolatie en afscherming om boogen, corrosie en elektromagnetische interferentie te voorkomen.
Testen en validatie:
- Voer grondig testen uit van ontwerpprestaties onder verschillende omstandigheden.
- Stresstests uitvoeren zoals temperatuurcycli, trillingstesten; Duurzaamheid beoordelen.
- Valideer de naleving van de industriële normen door rigoureuze testprotocollen.
Applicaties voor batterijpakket
- Portable Electronics: Batterijpakketten Power Mobile-apparaten zoals smartphones, tablets en laptops, die handige oplossingen op het gebied van GO bieden.
- Elektrische voertuigen: batterijpakketten zijn de primaire energieopslag in EV's, wat aandrijfkracht biedt voor emissievrij transport.
- Stationaire energieopslag: batterijpakketten slaan overtollige energie op uit hernieuwbare bronnen zoals zonne- en wind, waardoor back -upvermogen, rasterstabilisatie en load shifting mogelijk is.
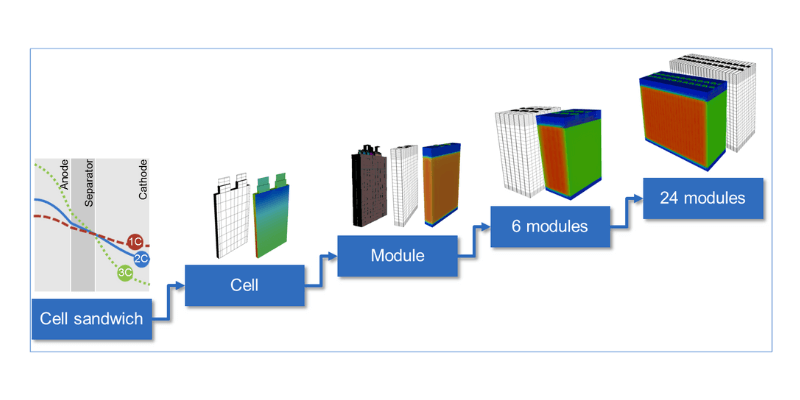
Wat is het verschil tussen batterijcellen, batterijmodule en batterij?
Om de verschillen tussen batterijcellen, modules en pakketten te begrijpen, laten we elke component afbreken:
- Batterijcel: de basiseenheid van energieopslag die chemische energie omzet in elektrische energie. Het wordt geleverd in verschillende vormen (cilindrisch, prismatisch of zakje) en bevat een anode, kathode, separator en elektrolyt.
- Batterijmodule: een groep onderling verbonden batterijcellen die de spanning en capaciteit verhoogt in vergelijking met individuele cellen. Het omvat bedrading en connectoren en kan een Basic Battery Management System (BMS) hebben voor monitoring.
- Batterij: een compleet energieopslagsysteem met een of meer modules. Het omvat een geavanceerd BMS voor celbalancering, temperatuurregeling en veiligheidsvoorzieningen, evenals extra componenten zoals behuizing en thermische beheersystemen.
Samenvatting:
- Batterijcel: de kleinste eenheid.
- Batterijmodule: een groep verbonden cellen.
- Batterij: een compleet systeem met modules en een BMS.
Analogie:
- Batterijcel: een enkele baksteen.
- Batterijmodule: een muur gemaakt van verschillende stenen.
- Batterij: een gebouw gemaakt van meerdere muren.