Choosing the right battery size is crucial for smooth operation and preventing damage to electrical components. Always double-check compatibility when replacing batteries in vehicles like cars, RVs, or boats. Familiarizing yourself with the Battery Group Size Chart is essential, as it provides information on polarity and dimensions such as width, height, and length. This article explores the battery size chart to help you select the perfect battery for your needs!
Why Standardization of Battery Sizes Matters
Battery size standardization ensures compatibility, safety, and ease of replacement across industries. For example, if your flashlight uses AA batteries and they run out, finding replacements is easy, but you need the exact same type and dimensions. AAA batteries won’t work despite similar voltage.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) sets standards for batteries and other electrical technologies. Non-rechargeable batteries follow IEC standard 60086, while rechargeable ones, like car batteries, adhere to IEC 60095.
Below is a detailed comparison of common household battery sizes:
| Battery Model | Battery Shape | Dimensions (mm) | Battery Voltage |
| AA | Cylinder | 50xdia.14.2 | 1.5 V |
| AAA | Cylinder | 44.5xdia.10.5 | 1.5 V |
| AAAA | Cylinder | 42xdia.8 | 1.5 V |
| C | Cylinder | 46xdia.26 | 1.5 V |
| D | Cylinder | 58xdia.33 | 1.5 V |
| 9V | Rectangle | 48.5×26.5×17.5 | 9V |
| 123 | Cylinder | 34.5xdia.17 | 3V |
| CR2 | Cylinder | 27.5xdia.16 | 3V |
| N | Cylinder | 30.2xdia.12 | 1.5 V |

Battery Sizes for Cars, RVs and Boats
The battery size in your car, RV, or boat significantly impacts its performance and overall capacity. To determine the right battery group size, it’s wise to check the manufacturer’s recommendations. You can also consult an expert to find the perfect fit for your vehicle. Below, we break down battery sizes for cars, RVs, and boats!
Battery Sizes for Cars and RVs
Automotive batteries are typically larger than household batteries. While some may be the same size, they are not interchangeable. Consult a manufacturer to select the appropriate battery size for your vehicle or RV, as an incorrect choice can damage the electrical system or impair performance.
A battery size chart can assist in selecting the right battery based on your car’s specifications, such as the one provided by Battery Council International (BCI).
| Group Size | Dimensions (mm) | Applications | Key Features |
| Group 24 | 260×173×225 | Compact cars, mid-sized sedans | Moderate CCA (500-800A) |
| Group 35 | 230×175×225 | Sedans, light trucks | High CCA (650-850A) |
| Group 48 (H6) | 278×175×190 | SUVs, luxury vehicles | Enhanced cold-cranking power |
| Group 65 | 306×192×192 | Trucks, high-performance vehicles | High RC (120-180 mins) |
Battery Sizes for Boats
When selecting the right battery size for your boat, consider the battery tray size, capacity, and any voltage adjustments.
Most boat batteries fall into Groups 24, 27, and 31. Here’s a handy chart for marine battery sizes:
| Group Size | Dimensions (mm) | Applications |
| Group 24 | 260×173×225 | Small boats, trolling motors |
| Group 27 | 306×173×225 | Mid-sized vessels |
| Group 31 | 330×173×240 | Large boats, solar backups |
What Are the Battery Group Sizes?
Battery group sizes, established by the Battery Council International (BCI), indicate battery dimensions and help identify suitable replacements. For example, if your old car battery is Group 27, you can buy any new Group 27 battery from any vendor. These classifications ensure compatibility in size and terminal placement for a secure fit.
You can check more details here.
How to Read the Battery Size Accurately
When choosing the right battery size for your needs, consider these four main factors:
1. Battery Group Numbers: These indicate the size and shape of the battery, ensuring it fits properly and aligns with the cables.
2. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This measures how well a battery can start an engine in cold weather; higher numbers mean better performance.
3. Terminal Position: The location of the terminals, whether on top or on the side, helps determine the required group size.
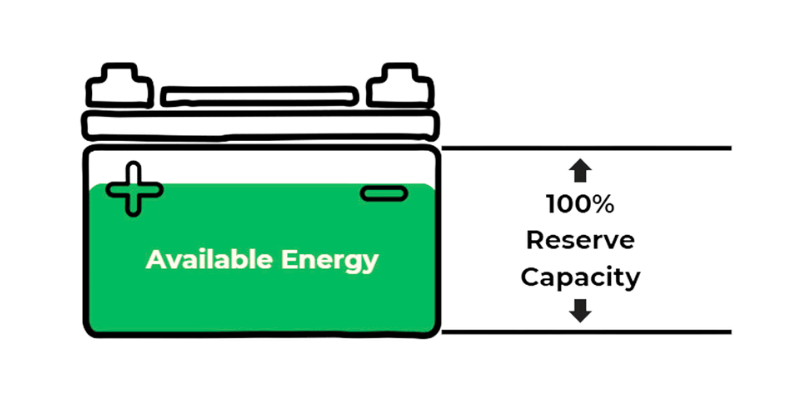
4. Reserve Capacity (RC): RC indicates how long a fully charged battery can power devices before running out, measured in minutes.
How to Select the Perfect Battery: 5-Step Checklist
1. Calculate Power Needs:
Use: Daily Watt-Hours = Device Wattage × Hours Used.
2. Match Group Size:
Measure compartment dimensions (L x W x H).
3. Prioritize Performance Metrics:
CCA for cold climates; RC for backup systems.
4. Check Compatibility:
Terminal placement (+/- alignment).
5. Compare Technologies:
Lithium for longevity; AGM for affordability.
Conclusion
Battery sizes vary by type, class, and purpose. When selecting a battery for your device, check the specifications to ensure safety and efficient performance. Use the charts above to determine the correct size for your car, RV, or boat.
FAQs
Can I replace a Group 24 battery with Group 27?
No, you need to make sure the dimensions and terminal placement align.
How can I ensure the battery fits my car using the size chart?
Check the size chart to see the group size suggested by the manufacturer. Ensure the terminal types and dimensions align for a proper fit!
Can I use the same size battery with a higher voltage?
No, use a higher voltage battery will damage your device. Stick with the battery recommended for your device or car.

