Battery power is now common in our daily lives, from smartphones to electric vehicles. A key battery component is the internal electrolyte, which keeps your devices running.
Today, let us explore what battery electrolyte is and how it works.
What Is Battery Electrolyte?
The battery electrolyte is the substance that transports positive ions between a battery’s two electrodes, enabling the battery to charge and discharge. The electrolyte can be a liquid or paste-like substance, depending on the battery type.
How Does Battery Electrolyte Work?
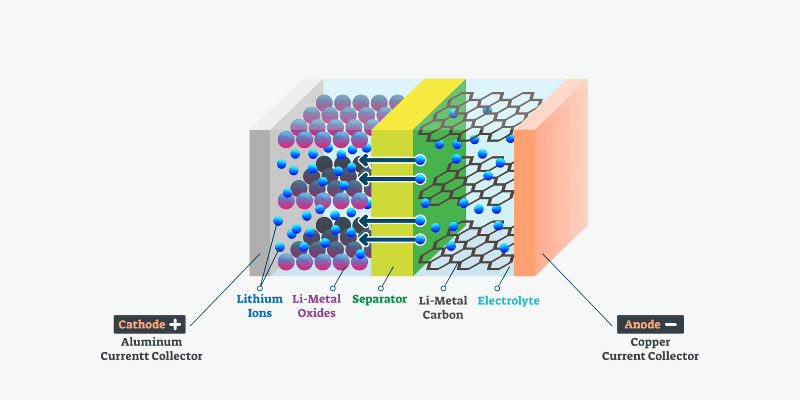
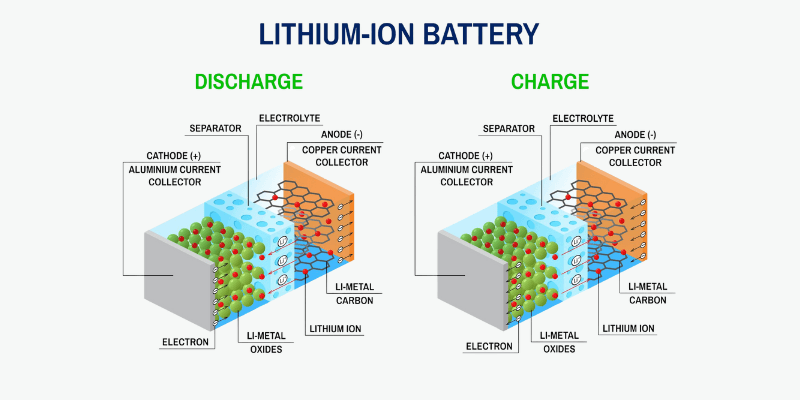
A battery has three key components: the cathode, anode and an electrolyte separating them. The electrolyte facilitates an electrical charge between the terminals, making the chemicals to react and convert stored energy into usable electricity for connected devices.
What Is the Battery Electrolyte Made Of?
Different batteries rely on different chemical reactions and electrolytes. Lead-acid batteries use sulfuric acid, zinc-air batteries oxidize zinc with oxygen, and alkaline batteries use potassium hydroxide. Lithium batteries commonly use a lithium salt solution, such as lithium hexafluorophosphate, as the electrolyte.
Can You Add Electrolyte To A Battery?
Yes, you can add water to a non-sealed wet cell battery. However, use only distilled water, as the battery consumes water, not sulfuric acid.
For sealed or non-off-gassing batteries, such as AGM or lithium-ion, don’t require electrolyte addition. Their lack of off-gassing is an advantage, as they need little maintenance once installed.
What Are the Ingredients in Lithium Battery Electrolytes?
Lithium battery electrolytes vary based on the battery chemistry and type. Most use a liquid electrolyte like LiPF6, LiBF4, or LiClO4 in an organic solvent.
However, solid ceramic electrolytes, such as lithium metal oxides, are an emerging option. Solid electrolytes eliminate the risks of leakage and flammability associated with liquid electrolytes.
Lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) is the most common lithium salt in lithium-ion batteries, creating a stable environment for lithium ions during use.
Is Lithium Battery Electrolyte Safe?
Early lithium batteries faced thermal runaway and fire risks due to overheating, punctures, or overcharging. But the electrolytes are safe.
As technology advances, new safety features like Holo Battery’s BMS can detect and shut down unsafe cells, making their batteries among the safest available.
Conclusion
Battery electrolyte is crucial for all battery types, though often overlooked.
Understanding how it works can extend battery life, especially for certain battery types.
Investing in products like Holo Battery’s custom lithium-ion batteries requires less maintenance, as the electrolyte is less of a concern.
Related Articles: